https://github.com/zq1997/deepin-wine
https://srf.baidu.com/site/guanwang_linux/index.html
您正在查看: Surou 发布的文章
《关于防范虚拟货币交易炒作风险的公告》
近期国务院金融稳定发展委员会再次明确针对虚拟币的严监管态度,中国互联网金融协会、中国银行业协会、中国支付清算协会联合发布了《关于防范虚拟货币交易炒作风险的公告》,BCSkill区块链中文技术社区成员必须严格遵守相关政策,社区内禁止一切虚拟货币交易炒作,如有不同意者请自行退出,如有违规,群管理有权立刻踢出。区块链技术社区存在的意义是为大家提供一个纯技术交流讨论和互相学习的环境。请大家珍惜一起学习的环境和机会。
Swarm项目和以太坊基金会的关系
trent.eth:“大约两年前的 2019 年,Swarm 团队从 EF 分拆为一个独立项目,我认为此时他们不会收到任何持续的资金”
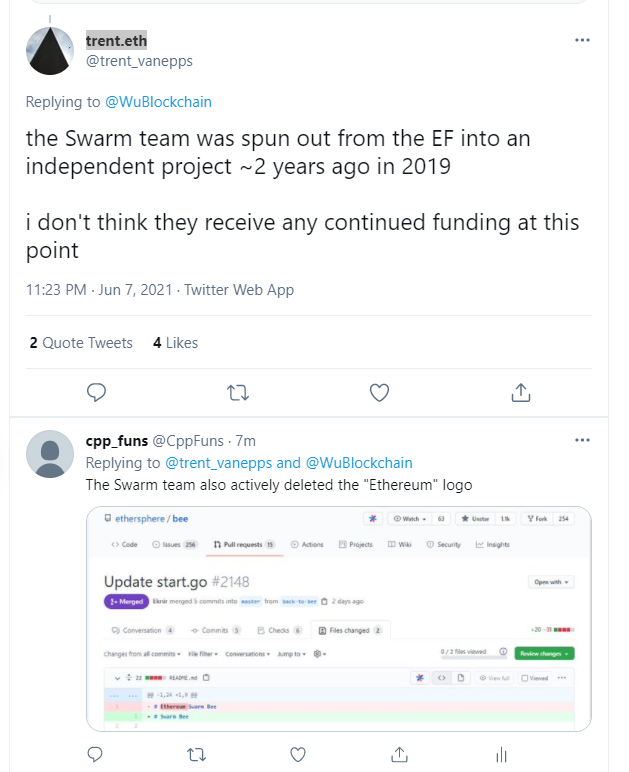
https://twitter.com/trent_vanepps/status/1401922884818321411
Swarm bee 开启mainnet方法
mainnet: true
network-id: 1
full-node: true
debug-api-enable: true
swap-enable: true
swap-endpoint: https://rpc.xdaichain.com
welcome-message: "https://www.bcskill.com"
db-open-files-limit: "500"
swap-initial-deposit: 0
verbosity: trace
api-addr: :1633
debug-api-addr: :1635
p2p-addr: :1634https://discord.com/channels/799027393297514537/810905662375854123/856719763454296094
最新回复
fzd: 请问这个解决了吗
StarkWare explained: layer 2 solution provider of dYdX and iMMUTABLE R11; BitKeep News: [...]Layer 2: https://...
一文读懂 StarkWare:dYdX 和 Immutable 背后的 L2 方案 R11; BitKeep 博客: [...]Layer 2:Comparing Laye...
http://andere.strikingly.com/: Regards, Great stuff!
surou: 需要先执行提案合约申请,等待出块节点地址同意后,才会进...
heco: WARN [11-19|11:26:09.459] N...
P: 你好,我在heco链上遇到了“tx fee excee...
Peng: 楼主安装成功了吗?我正在同步区块链,一天了,差不多才同...
joyhu: 你好,请问下安装好之后如何获取到bee.yaml配置文...
kaka: 支票最终怎么提币呢?
归档
April 2025March 2025February 2025January 2025December 2024November 2024October 2024September 2024August 2024July 2024June 2024May 2024April 2024March 2024January 2024December 2023November 2023October 2023September 2023August 2023July 2023June 2023April 2023March 2023February 2023January 2023December 2022November 2022October 2022August 2022July 2022June 2022May 2022March 2022February 2022January 2022December 2021November 2021October 2021September 2021August 2021July 2021June 2021May 2021April 2021March 2021February 2021January 2021December 2020November 2020October 2020September 2020July 2020June 2020May 2020April 2020March 2020February 2020January 2020December 2019November 2019October 2019September 2019August 2019July 2019June 2019May 2019April 2019March 2019February 2019January 2019December 2018November 2018October 2018September 2018August 2018July 2018June 2018