上一篇笔记中,写了nodeos的执行流程。nodeos使用的是一种插件体系,业务代码分布在一个个的插件类中,然后分析了插件类共的继承关系。本篇笔记,就从其中的net插件入手来分析p2p模块的功能,也就是分析学习net_plugin_impl类。同之前的笔记一样,从net插件的生命周期,初始化、启动、停止来分析,并重点分析p2p模块的运行状态。
一个区块链系统的p2p模块,应该包括以下几个职能:
(1)、从对等的节点那里,同步区块数据。
(2)、发送交易给其他节点进行验证。
(3)、验证其他节点发送过来的交易。
(3)、如果自己生产的区块,要发送区块给其他节点。
(4)、验证其他节点发送过来的区块。
1、net_plugin类的plugin_initialize方法(初始化)
此方法主要是用来使用命令行参数或者配置文件中的参数来配置net_plugin_impl类,该插件的业务主要在net_plugin_impl类中实现。下图为执行完plugin_initialize方法后的net_plugin_impl类对象

// 读取配置信息,初始化net_plugin_imul 对象的成员变量
peer_log_format = options.at( "peer-log-format" ).as<string>();
my->network_version_match = options.at( "network-version-match" ).as<bool>();
my->sync_master.reset( new sync_manager( options.at( "sync-fetch-span" ).as<uint32_t>()));
my->dispatcher.reset( new dispatch_manager );
my->connector_period = std::chrono::seconds( options.at( "connection-cleanup-period" ).as<int>());
my->max_cleanup_time_ms = options.at("max-cleanup-time-msec").as<int>();
my->txn_exp_period = def_txn_expire_wait;
my->resp_expected_period = def_resp_expected_wait;
my->dispatcher->just_send_it_max = options.at( "max-implicit-request" ).as<uint32_t>();
my->max_client_count = options.at( "max-clients" ).as<int>();
my->max_nodes_per_host = options.at( "p2p-max-nodes-per-host" ).as<int>();
my->num_clients = 0;
my->started_sessions = 0;
······
my->keepalive_timer.reset( new boost::asio::steady_timer( app().get_io_service()));
my->ticker(); //定时器,给每个连接发送时间戳`
plugin_initialize函数主要是初始化net_plugin_impl对象。并每隔32s给连接的节点发送心跳数据(时间戳数据),其中send_time发送是消息类型为该模块下定义的几种类型之一。
void net_plugin_impl::ticker() {
keepalive_timer->expires_from_now (keepalive_interval);
keepalive_timer->async_wait ([this](boost::system::error_code ec) {
ticker ();
if (ec) {
wlog ("Peer keepalive ticked sooner than expected: ${m}", ("m", ec.message()));
}
for (auto &c : connections ) {
if (c->socket->is_open()) {
c->send_time(); //遍历所有的连接,给每个连接定时发送时间戳message
}
}
});
}
2、net_plugin类的plugin_startup方法(启动运行)
plugin_startup方法是核心方法,包含了网络监听循环、接收数据处理、发送数据等内容。
等待连接部分:绑定、监听,在start_listen_loop函数里,等待其他节点的连接。通过boost::asio实现异步IO,不会阻塞。
if( my->acceptor ) {
//使用tcp:v4的协议 打开acceptor接收器
my->acceptor->open(my->listen_endpoint.protocol());
//设置地址复用 Address already in use
my->acceptor->set_option(tcp::acceptor::reuse_address(true));
try {
//绑定
my->acceptor->bind(my->listen_endpoint);
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
ilog("net_plugin::plugin_startup failed to bind to port ${port}",
("port", my->listen_endpoint.port()));
throw e;
}
//监听
my->acceptor->listen();
ilog("starting listener, max clients is ${mc}",("mc",my->max_client_count));
//接受连接 并处理发送过来的消息
my->start_listen_loop();
}
等待其他节点的连接
void net_plugin_impl::start_listen_loop( ) {
//获取单例模式中的io服务,并用其创建一个通信套接字。为什么不重新创建一个io服务?
auto socket = std::make_shared<tcp::socket>( std::ref( app().get_io_service() ) );
acceptor->async_accept( *socket, [socket,this]( boost::system::error_code ec ) {
if( !ec ) {
uint32_t visitors = 0; //统计共有多少个peer_addr变量为非空的连接
uint32_t from_addr = 0; //统计所有的连接里面,有几个是当前监听到的连接
auto paddr = socket->remote_endpoint(ec).address();
if (ec) {
fc_elog(logger,"Error getting remote endpoint: ${m}",("m", ec.message()));
}
else {
for (auto &conn : connections) { //遍历当前节点的所有连接
if(conn->socket->is_open()) {
if (conn->peer_addr.empty()) {
visitors++;
boost::system::error_code ec;
if (paddr == conn->socket->remote_endpoint(ec).address()) {
from_addr++;
}
}
}
}
//修改当前有效连接数
if (num_clients != visitors) {
ilog ("checking max client, visitors = ${v} num clients ${n}",("v",visitors)("n",num_clients));
num_clients = visitors;
}
//当前有效连接中不包含 新监听到的连接,则加入到有效连接里面,并启动一个会话
if( from_addr < max_nodes_per_host && (max_client_count == 0 || num_clients < max_client_count )) {
++num_clients;
connection_ptr c = std::make_shared<connection>( socket );
connections.insert( c );
start_session( c ); //重要 启动一个会话
}
else {
if (from_addr >= max_nodes_per_host) {
fc_elog(logger, "Number of connections (${n}) from ${ra} exceeds limit",
("n", from_addr+1)("ra",paddr.to_string()));
}
else {
fc_elog(logger, "Error max_client_count ${m} exceeded",
( "m", max_client_count) );
}
socket->close( );
}
}
} else {
elog( "Error accepting connection: ${m}",( "m", ec.message() ) );
// For the listed error codes below, recall start_listen_loop()
switch (ec.value()) {
case ECONNABORTED:
case EMFILE:
case ENFILE:
case ENOBUFS:
case ENOMEM:
case EPROTO:
break;
default:
return;
}
}
//继续等待下一个连接
start_listen_loop();
});
}
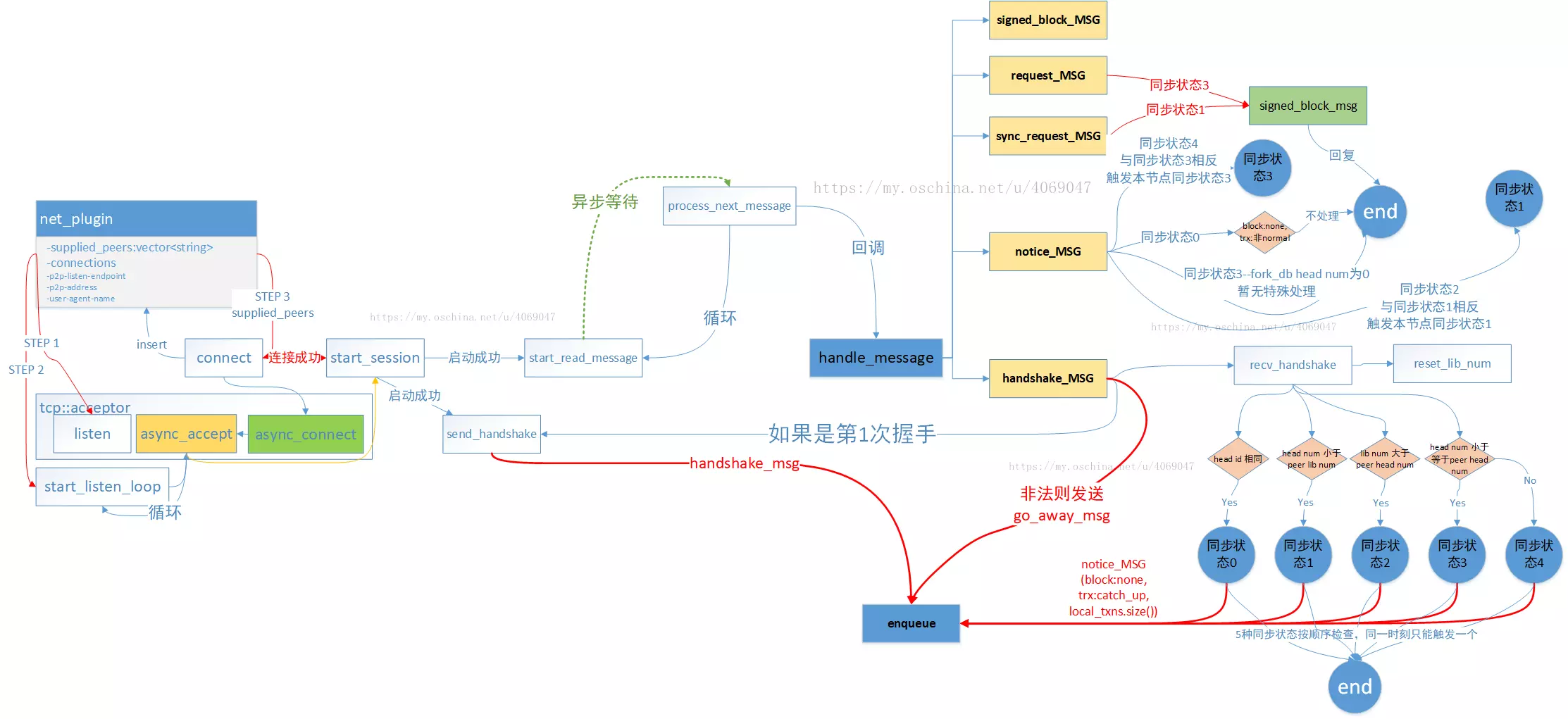
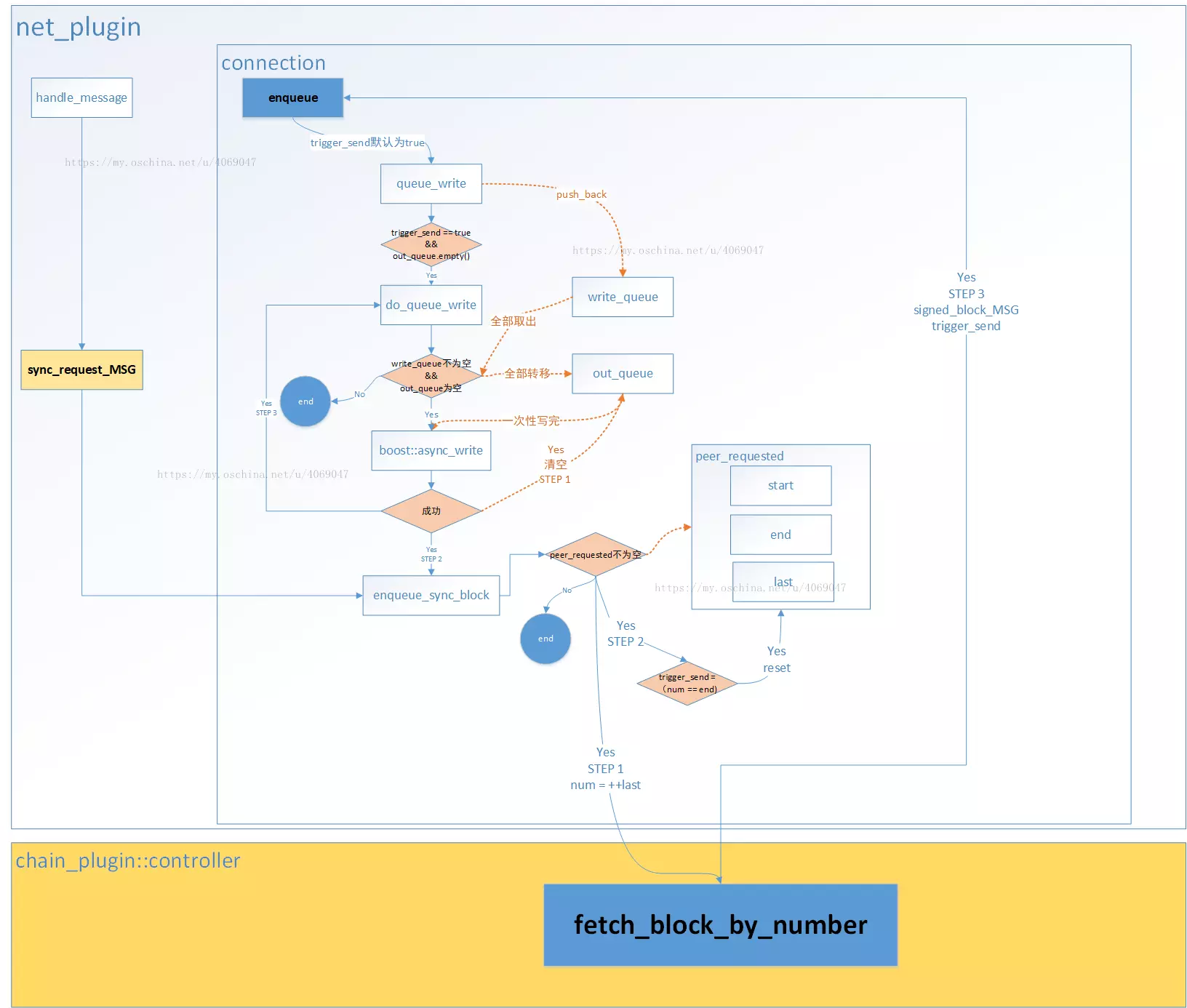
当接收到一个有效连接之后,开启一个会话,调用start_session方法,参数c为接受连接的套接字的指针,用来与连接到的节点收发数据。然后不断递归调用,接收下一个连接。其中start_session方法内部,主要是调用start_read_message( con )方法来处理消息的。所以我们需要重点查看start_read_message( con )函数。con和c指向的是同一个套接字。
void net_plugin_impl::start_read_message( connection_ptr conn ) {
try {
if(!conn->socket) { //验证套接字是否有效
return;
}
connection_wptr weak_conn = conn; //当前connection对象的一个weak_ptr指针
// 读取会递归调用,第一次读取时 outstanding_read_bytes未初始化,message_header_size初始化为4
std::size_t minimum_read = conn->outstanding_read_bytes ? *conn->outstanding_read_bytes : message_header_size;
if (use_socket_read_watermark) { //一种读取方式,根据node启动时的配置,水印优化读取??? 默认未开启
const size_t max_socket_read_watermark = 4096;
std::size_t socket_read_watermark = std::min<std::size_t>(minimum_read, max_socket_read_watermark);
boost::asio::socket_base::receive_low_watermark read_watermark_opt(socket_read_watermark);
conn->socket->set_option(read_watermark_opt);
}
auto completion_handler = [minimum_read](boost::system::error_code ec, std::size_t bytes_transferred) -> std::size_t {
if (ec || bytes_transferred >= minimum_read ) {
return 0;
} else {
return minimum_read - bytes_transferred;
}
};
//异步读取数据 pending_message_buffer为缓冲区
boost::asio::async_read(*conn->socket,
conn->pending_message_buffer.get_buffer_sequence_for_boost_async_read(), completion_handler,
[this,weak_conn]( boost::system::error_code ec, std::size_t bytes_transferred ) {
auto conn = weak_conn.lock(); //智能指针是否释放了
if (!conn) {
return;
}
conn->outstanding_read_bytes.reset(); //重置outstanding_read_bytes 表示字节数
try {
if( !ec ) {
//读取的字节数 大于可写入的字节数 错误
if (bytes_transferred > conn->pending_message_buffer.bytes_to_write()) {
elog("async_read_some callback: bytes_transfered = ${bt}, buffer.bytes_to_write = ${btw}",
("bt",bytes_transferred)("btw",conn->pending_message_buffer.bytes_to_write()));
}
EOS_ASSERT(bytes_transferred <= conn->pending_message_buffer.bytes_to_write(), plugin_exception, "");
// 根据读取的字节数,扩展buffer
conn->pending_message_buffer.advance_write_ptr(bytes_transferred);
while (conn->pending_message_buffer.bytes_to_read() > 0) { // buffer里面可读的字节数
uint32_t bytes_in_buffer = conn->pending_message_buffer.bytes_to_read();
//如果buffer里面的字节数小于 4个字节
if (bytes_in_buffer < message_header_size) {
conn->outstanding_read_bytes.emplace(message_header_size - bytes_in_buffer);
break;
} else {
uint32_t message_length;
// 返回当前读取的指针位置
auto index = conn->pending_message_buffer.read_index();
// 返回消息长度
conn->pending_message_buffer.peek(&message_length, sizeof(message_length), index);
// 消息长度过长或为0
if(message_length > def_send_buffer_size*2 || message_length == 0) {
boost::system::error_code ec;
elog("incoming message length unexpected (${i}), from ${p}", ("i", message_length)("p",boost::lexical_cast<std::string>(conn->socket->remote_endpoint(ec))));
close(conn);
return;
}
auto total_message_bytes = message_length + message_header_size;
//读取完一条消息
if (bytes_in_buffer >= total_message_bytes) {
conn->pending_message_buffer.advance_read_ptr(message_header_size);
if (!conn->process_next_message(*this, message_length)) {
return;
}
} else {
//未读取到某个类型消息结尾 循环重新读取
auto outstanding_message_bytes = total_message_bytes - bytes_in_buffer;
auto available_buffer_bytes = conn->pending_message_buffer.bytes_to_write();
if (outstanding_message_bytes > available_buffer_bytes) {
conn->pending_message_buffer.add_space( outstanding_message_bytes - available_buffer_bytes );
}
conn->outstanding_read_bytes.emplace(outstanding_message_bytes);
break;
}
}
}
start_read_message(conn);
} else {
auto pname = conn->peer_name();
if (ec.value() != boost::asio::error::eof) {
elog( "Error reading message from ${p}: ${m}",("p",pname)( "m", ec.message() ) );
} else {
ilog( "Peer ${p} closed connection",("p",pname) );
}
close( conn );
}
}
catch(const std::exception &ex) {
string pname = conn ? conn->peer_name() : "no connection name";
elog("Exception in handling read data from ${p} ${s}",("p",pname)("s",ex.what()));
close( conn );
}
catch(const fc::exception &ex) {
string pname = conn ? conn->peer_name() : "no connection name";
elog("Exception in handling read data ${s}", ("p",pname)("s",ex.to_string()));
close( conn );
}
catch (...) {
string pname = conn ? conn->peer_name() : "no connection name";
elog( "Undefined exception hanlding the read data from connection ${p}",( "p",pname));
close( conn );
}
} );
} catch (...) {
string pname = conn ? conn->peer_name() : "no connection name";
elog( "Undefined exception handling reading ${p}",("p",pname) );
close( conn );
}
}
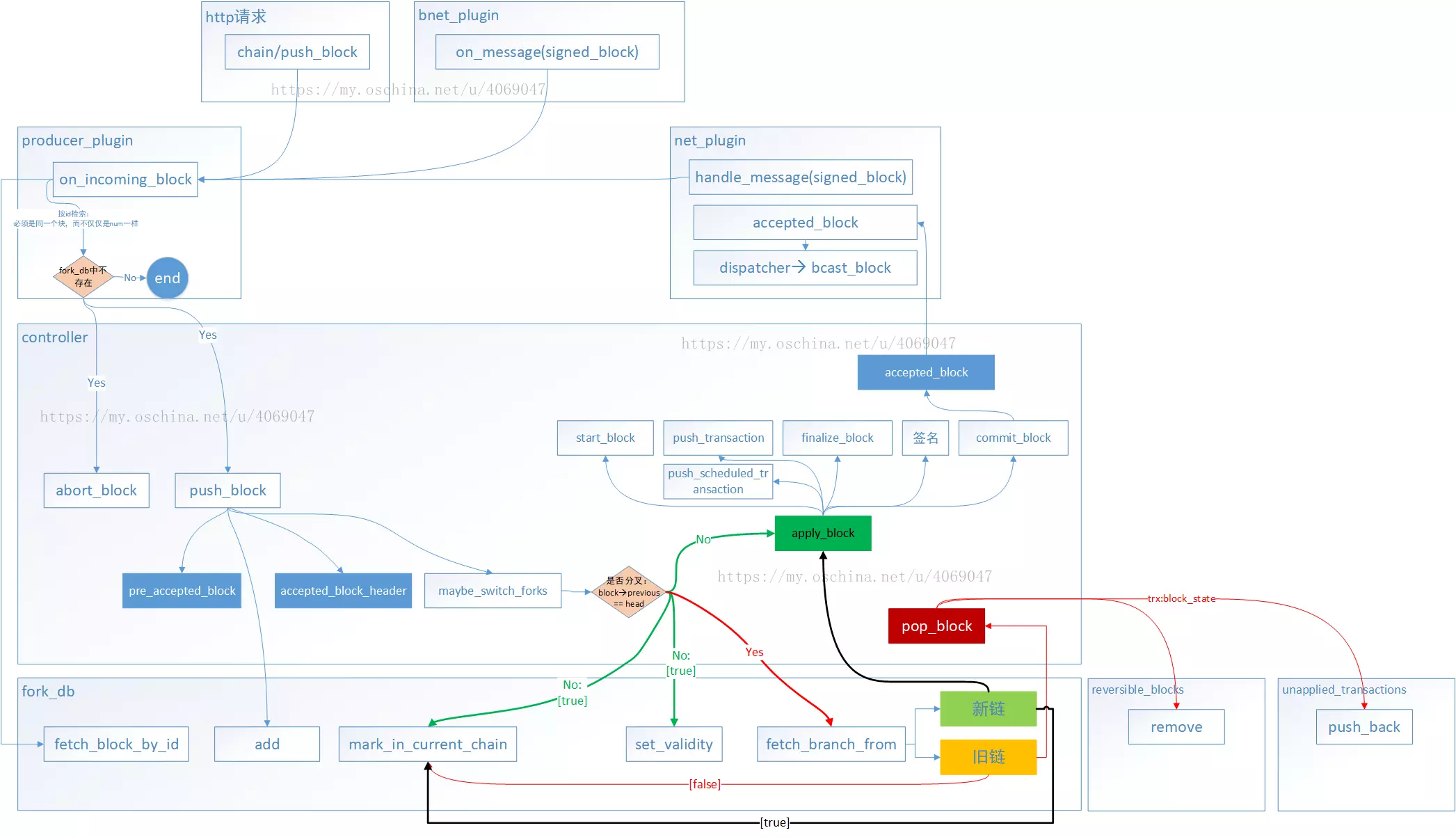
处理接收到的数据的函数比较长,基本重要的地方都标注了注释。该函数对接收数据的处理,主要是循环接收数据,并识别为要处理的消息类型,在eos系统下,通信的消息类型共分为如下几种,每种消息重载了一个handle_message函数来处理。在process_next_message函数里面进行消息分发。
handshake_message, 握手消息类型
chain_size_message, 未使用
go_away_message, 退出连接消息类型
time_message, 时间戳消息类型
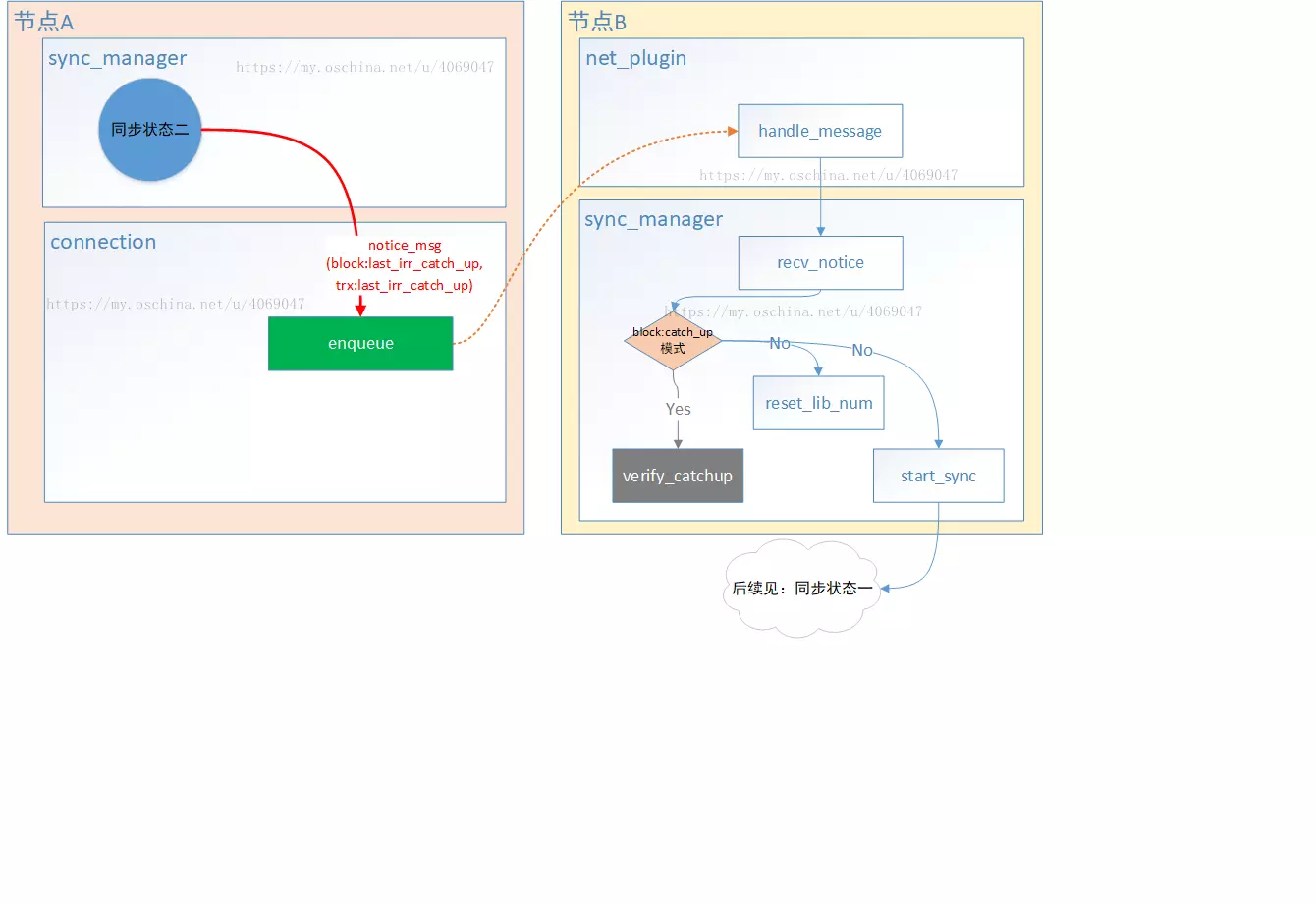
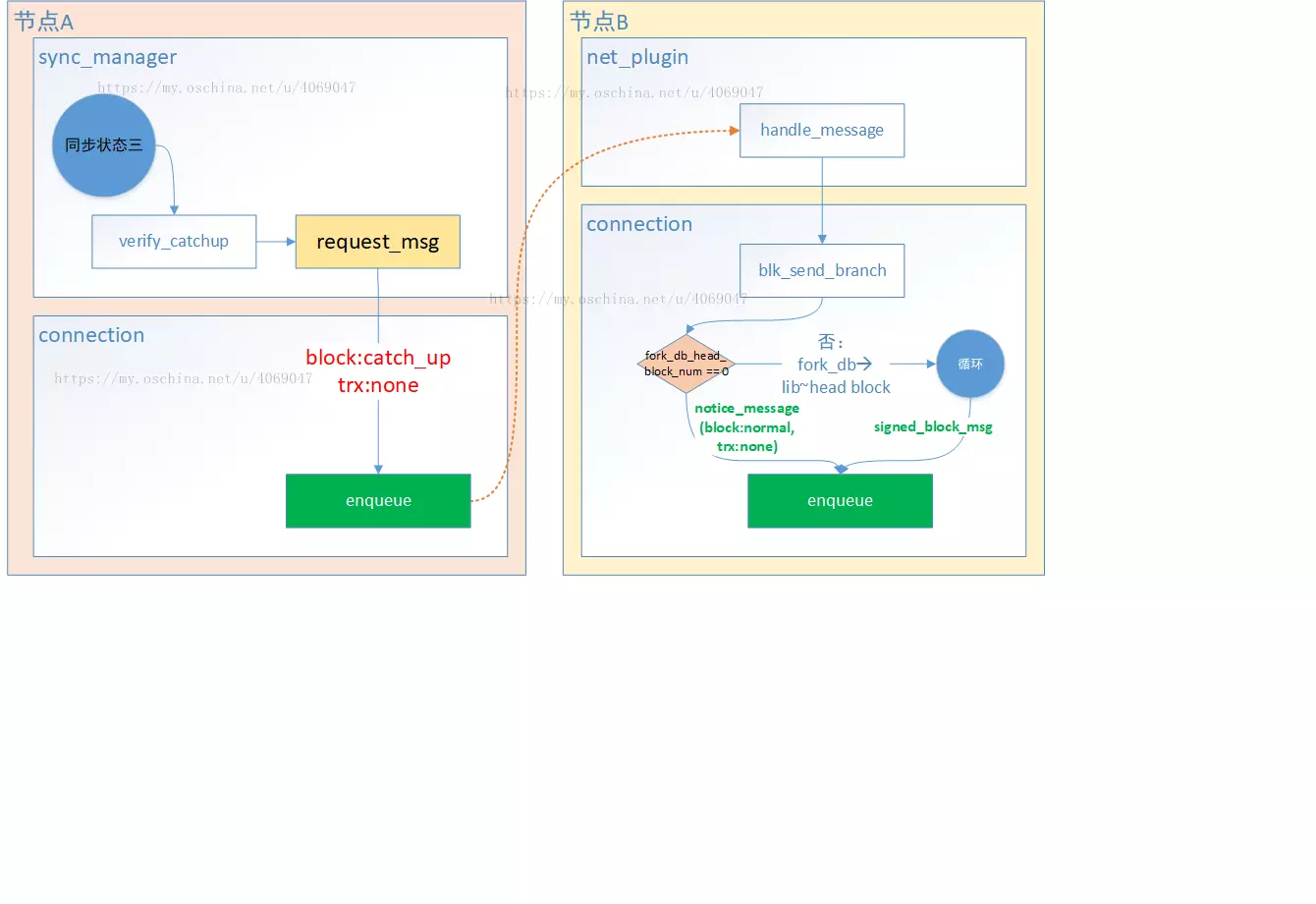
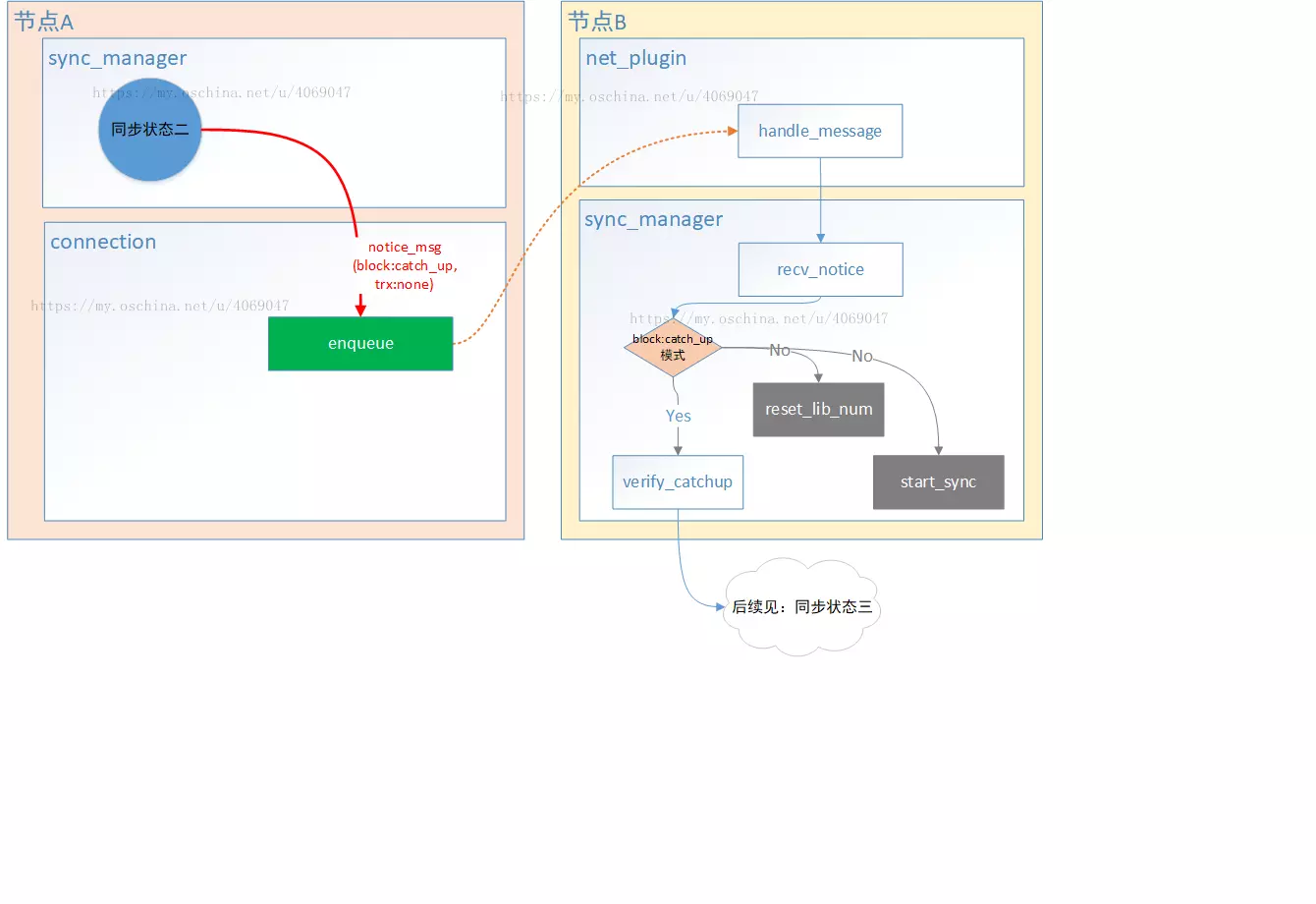
notice_message, 通知消息类型,在区块同步中,该类型包含了区块状态等信息
request_message, 同步区块
sync_request_message, 同步区块
signed_block, 区块详细数据
packed_transaction 打包交易
bool connection:: process_next_message(net_plugin_impl& impl, uint32_t message_length) {
try {
// If it is a signed_block, then save the raw message for the cache
// This must be done before we unpack the message.
// This code is copied from fc::io::unpack(..., unsigned_int)
auto index = pending_message_buffer.read_index();
uint64_t which = 0; char b = 0; uint8_t by = 0;
do {
pending_message_buffer.peek(&b, 1, index);
which |= uint32_t(uint8_t(b) & 0x7f) << by;
by += 7;
} while( uint8_t(b) & 0x80 && by < 32); //如果是block,是签名的,需要先验证签名,再解压,其他消息类型随意。
if (which == uint64_t(net_message::tag<signed_block>::value)) { // 验证签名 读取下一个消息
blk_buffer.resize(message_length);
auto index = pending_message_buffer.read_index();
pending_message_buffer.peek(blk_buffer.data(), message_length, index);
}
auto ds = pending_message_buffer.create_datastream();
net_message msg;
fc::raw::unpack(ds, msg); //解压缩message消息
msgHandler m(impl, shared_from_this() );
msg.visit(m); //调用的是net_plugin_impl 的成员函数handle_message
} catch( const fc::exception& e ) {
edump((e.to_detail_string() ));
impl.close( shared_from_this() );
return false;
}
return true;
}
重载的消息处理函数(具体发送的数据类型,下一篇笔记在详细写,目前还没有调试明白)
void handle_message( connection_ptr c, const notice_message &msg);
void handle_message( connection_ptr c, const request_message &msg);
void handle_message( connection_ptr c, const sync_request_message &msg);
void handle_message( connection_ptr c, const signed_block &msg);
void handle_message( connection_ptr c, const packed_transaction &msg);
除了监听等待连接之外,该插件启动后也会向其他节点发送数据,发送数据部分:
my->start_monitors();
for( auto seed_node : my->supplied_peers ) {
connect( seed_node );
}
if(fc::get_logger_map().find(logger_name) != fc::get_logger_map().end())
logger = fc::get_logger_map()[logger_name];
start_monitors启动两个监控,监控新加入的连接,监控过期的交易,并移除(此种方式没有太理解,后面分析到chain插件的时候,再回过头来看)。
void net_plugin_impl::start_monitors() {
connector_check.reset(new boost::asio::steady_timer( app().get_io_service()));
transaction_check.reset(new boost::asio::steady_timer( app().get_io_service()));
start_conn_timer(connector_period, std::weak_ptr<connection>());
start_txn_timer();
}
之后for循环,连接到seed节点。connect函数重载了两个,一个接受节点信息为参数,另一个实现具体业务逻辑。
void net_plugin_impl::connect( connection_ptr c ) {
if( c->no_retry != go_away_reason::no_reason) {
fc_dlog( logger, "Skipping connect due to go_away reason ${r}",("r", reason_str( c->no_retry )));
return;
}
auto colon = c->peer_addr.find(':');
if (colon == std::string::npos || colon == 0) {
elog ("Invalid peer address. must be \"host:port\": ${p}", ("p",c->peer_addr));
for ( auto itr : connections ) {
if((*itr).peer_addr == c->peer_addr) {
(*itr).reset();
close(itr);
connections.erase(itr);
break;
}
}
return;
}
auto host = c->peer_addr.substr( 0, colon );
auto port = c->peer_addr.substr( colon + 1);
idump((host)(port));
tcp::resolver::query query( tcp::v4(), host.c_str(), port.c_str() );
connection_wptr weak_conn = c;
// Note: need to add support for IPv6 too
//异步解析seed节点
resolver->async_resolve( query,
[weak_conn, this]( const boost::system::error_code& err,
tcp::resolver::iterator endpoint_itr ){
auto c = weak_conn.lock();
if (!c) return;
if( !err ) {
connect( c, endpoint_itr ); //调用重载函数,实现内部逻辑
} else {
elog( "Unable to resolve ${peer_addr}: ${error}",
( "peer_addr", c->peer_name() )("error", err.message() ) );
}
});
}
//重载之后的connect,实现了异步连接到其他节点
void net_plugin_impl::connect( connection_ptr c, tcp::resolver::iterator endpoint_itr ) {
if( c->no_retry != go_away_reason::no_reason) {
string rsn = reason_str(c->no_retry);
return;
}
auto current_endpoint = *endpoint_itr;
++endpoint_itr;
c->connecting = true;
connection_wptr weak_conn = c;
c->socket->async_connect( current_endpoint, [weak_conn, endpoint_itr, this] ( const boost::system::error_code& err ) {
auto c = weak_conn.lock();
if (!c) return;
if( !err && c->socket->is_open() ) {
if (start_session( c )) {
c->send_handshake (); //连接上之后,给其他节点发送握手消息,可见握手消息是非常重要的,下一步重要调试握手消息的报文内容
}
} else {
if( endpoint_itr != tcp::resolver::iterator() ) {
close(c);
connect( c, endpoint_itr );
}
else {
elog( "connection failed to ${peer}: ${error}",
( "peer", c->peer_name())("error",err.message()));
c->connecting = false;
my_impl->close(c);
}
}
} );
}
//握手消息报文结构
struct handshake_message {
uint16_t network_version = 0; ///< incremental value above a computed base
chain_id_type chain_id; ///< used to identify chain
fc::sha256 node_id; ///< used to identify peers and prevent self-connect
chain::public_key_type key; ///< authentication key; may be a producer or peer key, or empty
tstamp time;
fc::sha256 token; ///< digest of time to prove we own the private key of the key above
chain::signature_type sig; ///< signature for the digest
string p2p_address;
uint32_t last_irreversible_block_num = 0;
block_id_type last_irreversible_block_id;
uint32_t head_num = 0;
block_id_type head_id;
string os;
string agent;
int16_t generation;
};
3、net_plugin类的plugin_shutdown方法(停止)
plugin_shutdown方法主要功能是关闭监听接收器,循环关闭每个连接,释放资源,代码较少,如下所示:
void net_plugin::plugin_shutdown() {
try {
ilog( "shutdown.." );
my->done = true;
if( my->acceptor ) {
ilog( "close acceptor" );
my->acceptor->close();
ilog( "close ${s} connections",( "s",my->connections.size()) );
auto cons = my->connections;
for( auto con : cons ) {
my->close( con);
}
my->acceptor.reset(nullptr);
}
ilog( "exit shutdown" );
}
FC_CAPTURE_AND_RETHROW()
}
转载自:
https://github.com/RootkitKiller/EosLearn/blob/master/Eos%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0%EF%BC%88%E4%B8%89%EF%BC%89net_plugin%E6%8F%92%E4%BB%B6%E8%AF%A6%E7%BB%86%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90.md