Table of Content
总览
本文主要致力于EOS区块结构、生产、打包、验证、存储等流程分析,当然其他部分源码也有涉及,但在此不做详细讨论。
环境
Mac OS High Sierra 10.13.6
EOS源码版本1.2.1
CLion
CMake
预备知识
chain分析
blockchain基本数据结构
区块结构:
- block_header,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/block_header.hpp第7行
struct block_header {
block_timestamp_type timestamp; //区块产生时间
account_name producer; //区块生产者
uint16_t confirmed = 1; //dpos确认数
block_id_type previous; //前一个区块的头的hash值
checksum256_type transaction_mroot; //区块包含的transactions的merkel树根
checksum256_type action_mroot; //区块包含的actions的merkel树根,这些actions实际包含在transactions中
uint32_t schedule_version = 0;
optional<producer_schedule_type> new_producers;
extension_type header_extension;
}
- signed_block_header,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/block_header.hpp第45行
struct signed_block_header : public block_header {
signature_type producer_signature; //生产者的签名
}
- signed_block,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/block.hpp 57行
struct signed_block : public signed_block_header {
vector<transacton_receipt> transactions; //区块包含的transactions执行后得到的回执
extrension_type block_extensions;
}
- transaction_receipt_header,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/block.hpp 12行
struct transaction_receipt_header {
enum status_enum {
executed = 0, //transaction成功执行,没有错误发生
soft_fail = 1, //
hard_fail = 2,
delayed = 3,
expired = 4
};
fc::enum_type<uint8_t,status_enum> status;
uint32_t cpu_usage_us; //总CPU使用时间,单位为微秒
fc::unsigned_int net_usage_words;//总网络使用量
}
- transaction_receipt,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/block.hpp 33行
struct transaction_receipt : public transaction_receipt_header {
fc::static_variant<transaction_id_type,packed_transaction> trx; //已经执行过的transactions
}
- transaction_header,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/transaction.hpp 30行
struct transaction_header {
time_point_sec expiration; //过期时间
uint16_t ref_block_num = 0U; //用于TaPos验证
uint32_t ref_block_prefix = 0UL; //用于TaPos验证
fc::unsigned_int max_net_usage_words = 0UL;
uint8_t max_cpu_usage_ms = 0;
fc::unsigned_int delay_sec;
}
- transaction,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/transaction.hpp 54行
struct transaction : public transaction_header {
vector<action> context_free_actions; //上下文无关的actions
vector<action> actions;
extension_type transaction_extensions;
}
- signed_transaction,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/transaction.hpp 78行
struct signed_transaction : public transaction {
vector<signature> signatures;
vector<bytes> context_free_data; //和context_free_action一一对应
}
- packed_transaction,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/transaction.hpp 98行
struct packed_transaction {
enum compression_type {
none = 0,
zlib = 1
}
vector<signature_type> signatures;
fc::enum_type<uint8_t,compression_type> compression;
bytes packed_context_free_data;
bytes packed_trx;
}
- deferred_transaction,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/transaction.hpp 157行
struct deferred_transaction : public signed_transaction {
uint128_t sender_id;
account_name sender;
account_name payer;
time_point_sec execute_after;
}
- action,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/action.hpp 60行
struct action {
account_name account;
action_name name;
vector<permission_level> authorization;
bytes data;
}
- pending_state,定义在:libraries/chain/controller.cpp 91行,这是区块生产过程和区块同步过程中一个非常关键的数据结构
struct pending_state {
maybe_session _db_session; //数据库session,主要涉及undo,squash,push相关操作,使数据库undo_state处于正确状态
block_state_ptr _pending_block_state;
vector<action_receipt> _actions; //transactions在执行过程中生成的action_receipt,会打包到区块中(finalize_block)
controller::block_status _block_status;
}
-
block_header_state,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/block_header_state.hpp 11行
这个结构定义了验证transaction所需的头部信息,以及生成一个新的block所需的信息
struct block_header_state {
block_id_type id;//最近的block_id
uint32_t block_num = 0;//最近的block的高度/值
signed_block_header header; //最近的block header;
uint32_t dpos_proposed_irreversible_blocknum = 0;//最新的被提出dpos不可逆的区块高度/值,需要dpos计算确认
uint32_t dpos_irreversible_blocknum = 0;//最新的dpos不可逆区块高度/值,这个是已经确认了的
uint32_t bft_irreversible_block = 0; //bft不可逆区块高度/值
uint32_t pending_schedule_lib_num; //
digest_type pending_schedule_hash;
producer_schedule_type pending_schedule;
producer_schedule_type active_schedule;
incremental_merkel block_root_merkle;
flat_map<account_name,uint32_t> producer_to_last_produced;
flat_map<account_name,uint32_t> procuer_to_last_implied_irb;
public_key_type block_signing_key; //当前生产者的签名
vector<uint8_t> confirm_count;
vector<header_confirmation> confirmations;
}
-
block_state,定义在:libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/block_state.hpp 14行
struct block_state : public block_header_state {
signed_block_ptr block; //前一个block指针
bool validated = false;
bool in_current_chain = false;
}
-
以上为EOS区块的关键数据结构,下面的分析都是围绕着以上的数据结构来进行的。数据结构之间的关系如下: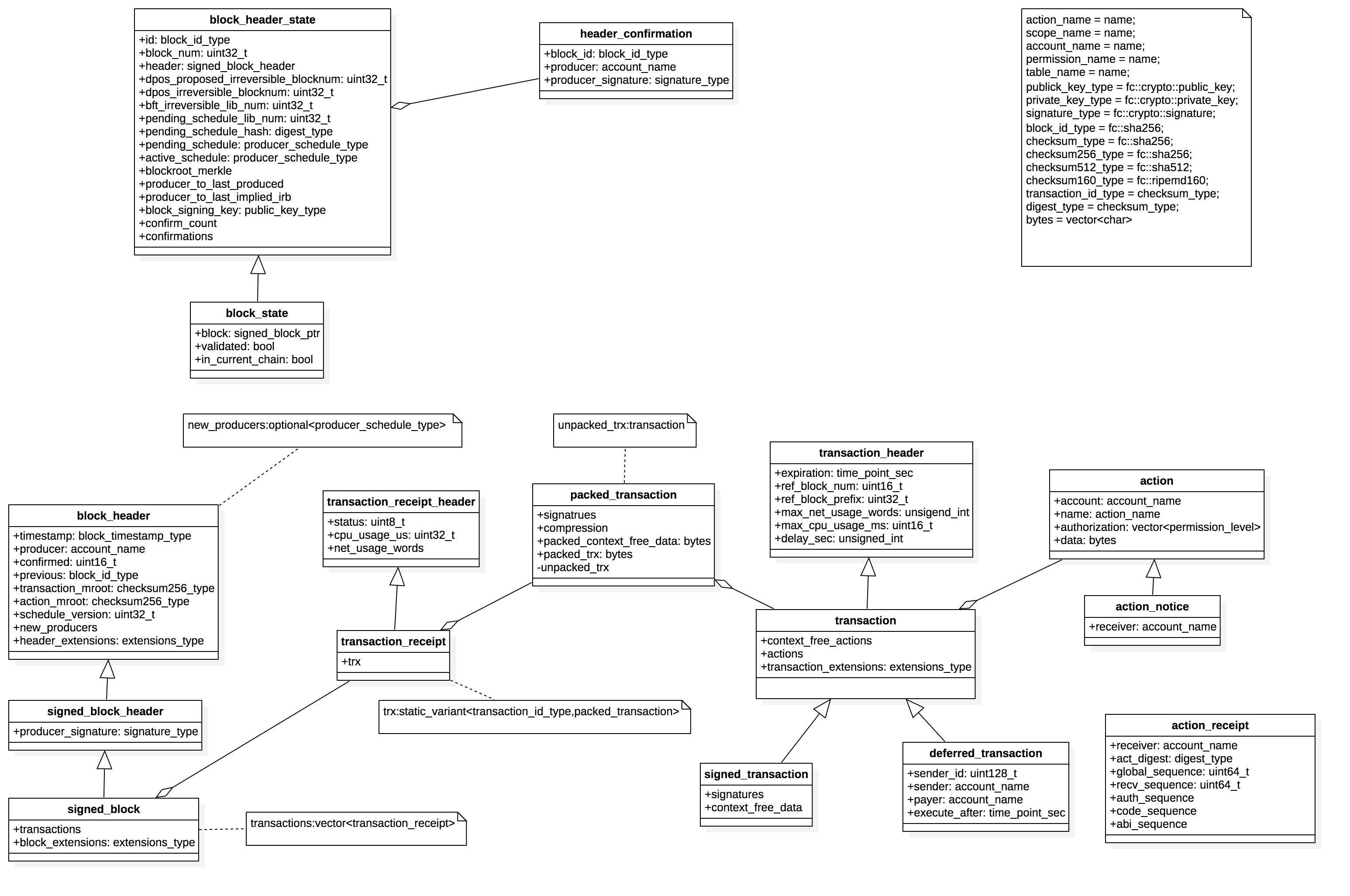
producer_plugin
producer_plugin实现了区块生产和区块同步的调用功能。
头文件定义在:plugins/producer_plugin/include/eosio/producer_plugin/producer_plugin.hpp
实现文件定义在:plugins/producer_plugin/producer_plugin.cpp
开始插件系统会调用producer_plugin::set_program_options函数进行相关程序项的设置:
- 生成config.ini文件(如果该文件不存在的话)
- 读取配置
调用producer_plugin::plugin_initialize函数进行初始化工作:
- 初始化配置
- 设置信号函数
调用producer_plugin::plugin_start函数,主要完成的功能如下:
- 设置信号函数:
my->_accepted_block_connection.emplace(chain.accepted_block.connect( [this]( const auto& bsp ){ my->on_block( bsp ); } ));
my->_irreversible_block_connection.emplace(chain.irreversible_block.connect( [this]( const auto& bsp ){ my->on_irreversible_block( bsp->block ); } ));
- 获取最新的不可逆的区块号
- 进入生产区块的调度 producer_plugin_impl::schedule_production_loop
producer_plugin_impl::schedule_production_loop:
- 取消前一次的_timer操作:
chain::controller& chain = app().get_plugin<chain_plugin>().chain();
_timer.cancel();
std::weak_ptr<producer_plugin_impl> weak_this = shared_from_this();
- 调用 result = start_block(bool &last_block),函数定义在plugins/producer_plugin/producer_plugin.cpp 882行:
在该函数中:
- 首先会取得chain::controller的引用chain,判断chain当前的数据库模式是否为db_read_mode::READ_ONLY,如果是则返回状态start_block_result::waiting;如果不是则将当前的_pending_block_mode设为pending_block_mode::producing:
chain::controller& chain = app().get_plugin<chain_plugin>().chain();
if( chain.get_read_mode() == chain::db_read_mode::READ_ONLY )
return start_block_result::waiting;
- 计算当前节点是否为生产节点,获取当前被调度的生产者的watermark和signature:
last_block = ((block_timestamp_type(block_time).slot % config::producer_repetitions) == config::producer_repetitions - 1);
const auto& scheduled_producer = hbs->get_scheduled_producer(block_time);
auto currrent_watermark_itr = _producer_watermarks.find(scheduled_producer.producer_name);
auto signature_provider_itr = _signature_providers.find(scheduled_producer.block_signing_key);
auto irreversible_block_age = get_irreversible_block_age();
- 进行一系列的条件判断:
检查当前节点是否被允许生产、被调度的生产者是否在生产队列中等:if( !_production_enabled ) {
_pending_block_mode = pending_block_mode::speculating;
} else if( _producers.find(scheduled_producer.producer_name) == _producers.end()) {
_pending_block_mode = pending_block_mode::speculating;
} else if (signature_provider_itr == _signature_providers.end()) {
elog("Not producing block because I don't have the private key for ${scheduled_key}", ("scheduled_key", scheduled_producer.block_signing_key));
_pending_block_mode = pending_block_mode::speculating;
} else if ( _pause_production ) {
elog("Not producing block because production is explicitly paused");
_pending_block_mode = pending_block_mode::speculating;
} else if ( _max_irreversible_block_age_us.count() >= 0 && irreversible_block_age >= _max_irreversible_block_age_us ) {
elog("Not producing block because the irreversible block is too old [age:${age}s, max:${max}s]", ("age", irreversible_block_age.count() / 1'000'000)( "max", _max_irreversible_block_age_us.count() / 1'000'000 ));
_pending_block_mode = pending_block_mode::speculating;
}
- 判断start_block返回值:
-
result == failed
start pending block 失败,稍后再试.启动定时器_timer,等待50ms再次进入schedule_production_loop
if (result == start_block_result::failed) {
elog("Failed to start a pending block, will try again later");
_timer.expires_from_now( boost::posix_time::microseconds( config::block_interval_us / 10 ));
// we failed to start a block, so try again later?
//启动定时器,待会儿再试
_timer.async_wait([weak_this,cid=++_timer_corelation_id](const boost::system::error_code& ec) {
auto self = weak_this.lock();
if (self && ec != boost::asio::error::operation_aborted && cid == self->_timer_corelation_id) {
self->schedule_production_loop();
}
});
}
-
result == waiting
调用producer_plugin_impl::schedule_delayed_production
if (result == start_block_result::waiting){
//这里检查生产者队列是否为空和是否被允许生产
if (!_producers.empty() && !production_disabled_by_policy()) {
fc_dlog(_log, "Waiting till another block is received and scheduling Speculative/Production Change");
schedule_delayed_production_loop(weak_this, calculate_pending_block_time());
} else {
fc_dlog(_log, "Waiting till another block is received");
// nothing to do until more blocks arrive
}
}
-
_pending_block_mode == producint && result == successed
启动定时器,在若干毫秒之后调用producer_plugin_impl::maybe_produce_block进行区块生产的完成工作,在这个时间段内当前节点收到的所有transaction都会被打进这个区块中。
if (_pending_block_mode == pending_block_mode::producing) {
// we succeeded but block may be exhausted
static const boost::posix_time::ptime epoch(boost::gregorian::date(1970, 1, 1));
if (result == start_block_result::succeeded) {
// ship this block off no later than its deadline
_timer.expires_at(epoch + boost::posix_time::microseconds(chain.pending_block_time().time_since_epoch().count() + (last_block ? _last_block_time_offset_us : _produce_time_offset_us)));
fc_dlog(_log, "Scheduling Block Production on Normal Block #${num} for ${time}", ("num", chain.pending_block_state()->block_num)("time",chain.pending_block_time()));
} else {
auto expect_time = chain.pending_block_time() - fc::microseconds(config::block_interval_us);
// ship this block off up to 1 block time earlier or immediately
if (fc::time_point::now() >= expect_time) {
_timer.expires_from_now( boost::posix_time::microseconds( 0 ));
} else {
_timer.expires_at(epoch + boost::posix_time::microseconds(expect_time.time_since_epoch().count()));
}
fc_dlog(_log, "Scheduling Block Production on Exhausted Block #${num} immediately", ("num", chain.pending_block_state()->block_num));
}
_timer.async_wait([&chain,weak_this,cid=++_timer_corelation_id](const boost::system::error_code& ec) {
auto self = weak_this.lock();
if (self && ec != boost::asio::error::operation_aborted && cid == self->_timer_corelation_id) {
auto res = self->maybe_produce_block();
fc_dlog(_log, "Producing Block #${num} returned: ${res}", ("num", chain.pending_block_state()->block_num)("res", res) );
}
});
}
- producer_plugin_impl::maybe_produce_block,这个函数会调用producer_plugin_impl::produce_block完成区块生产:
//确保在异常退出候,scheudle_production_loop依然能够正常进行下去
auto reschedule = fc::make_scoped_exit([this]{
schedule_production_loop();
});
try {
//完成区块的finalize_block,区块签名,更新fork_db
produce_block();
return true;
} catch ( const guard_exception& e ) {
app().get_plugin().handle_guard_exception(e);
return false;
} catch ( boost::interprocess::bad_alloc& ) {
raise(SIGUSR1);
return false;
} FC_LOG_AND_DROP();
fc_dlog(_log, "Aborting block due to produce_block error");
chain::controller& chain = app().get_plugin().chain();
chain.abort_block();
return false;
5. producer_plugin_impl::produce_block函数主要完成区块生产的主要工作包括:
* finalize_block:
更新资源限制
设置action merkle树根
设置transaction merkle树根
...在controller中有更详细说明
* sign_block
对block进行签名,防止被篡改
* commit_block
将新产生的区块加到数据库中,并将该区块广播出去。在controller有详细叙述
```cpp
EOS_ASSERT(_pending_block_mode == pending_block_mode::producing, producer_exception, "called produce_block while not actually producing");
chain::controller& chain = app().get_plugin<chain_plugin>().chain();
const auto& pbs = chain.pending_block_state();
const auto& hbs = chain.head_block_state();
EOS_ASSERT(pbs, missing_pending_block_state, "pending_block_state does not exist but it should, another plugin may have corrupted it");
auto signature_provider_itr = _signature_providers.find( pbs->block_signing_key );
EOS_ASSERT(signature_provider_itr != _signature_providers.end(), producer_priv_key_not_found, "Attempting to produce a block for which we don't have the private key");
//idump( (fc::time_point::now() - chain.pending_block_time()) );
//完成块
chain.finalize_block();
//对块进行签名
chain.sign_block( [&]( const digest_type& d ) {
auto debug_logger = maybe_make_debug_time_logger();
return signature_provider_itr->second(d);
} );
//提交块到数据库
chain.commit_block();
auto hbt = chain.head_block_time();
//idump((fc::time_point::now() - hbt));
block_state_ptr new_bs = chain.head_block_state();
_producer_watermarks[new_bs->header.producer] = chain.head_block_num();
ilog("Produced block ${id}... #${n} @ ${t} signed by ${p} [trxs: ${count}, lib: ${lib}, confirmed: ${confs}]",
("p",new_bs->header.producer)("id",fc::variant(new_bs->id).as_string().substr(0,16))
("n",new_bs->block_num)("t",new_bs->header.timestamp)
("count",new_bs->block->transactions.size())("lib",chain.last_irreversible_block_num())("confs", new_bs->header.confirmed));
至此producer_plugin中区块的生产流程已经介绍完毕,更详细的分析会在controller中体现出来。 总体时序如下:

区块同步流程:
controller
producer_plugin在区块生产的过程中扮演着调度的角色,而实际工作是放在controller中来完成的,下面将纤细分析controller在区块生成过程中所扮演的角色功能:
上文说到在producer_plugin_impl::start_block函数中会调用controller::abort_block和controller::start_block两个函数,这里需要展示一下controller相关数据结构,controller的功能主要是在controller_impl中实现的,这里只列举关键部分:
struct controller {
enum class block_status {
irreversible = 0, //区块已经被应用,且不可逆
validated = 1, //区块已经被可信任的生产者签名,并已经应用但还不是不可逆状态
complete = 2, //区块已经被可信任的生产者签名,但是还没有被应用,状态为可逆
incomplete = 3 //区块正在生产过程
};
//信号量集合
signal<void(const signed_block_ptr&)> pre_accepted_block;
signal<void(const block_state_ptr&)> accepted_block_header;
signal<void(const block_state_ptr&)> accepted_block;
signal<void(const block_state_ptr&)> irreversible_block;
signal<void(const transaction_metadata_ptr&)> accepted_transaction;
signal<void(const transaction_trace_ptr&)> applied_transaction;
signal<void(const header_confirmation&)> accepted_confirmation;
signal<void(const int&)> bad_alloc;
private:
std::unique_ptr<controller_impl> my;
};
struct controller_impl {
controller& self;
chainbase::database db; // state db,主要是存储合约执行后的各种状态信息
chainbase::database reversible_blocks; //用来存储已经成功应用但是还是可逆状态
block_log blog;
optional<pending_state> pending; //保存正在生成的block信息,该结构在上文已经列出
block_state_ptr head; //上一次block state信息,该结构在上文已经列出
fork_database fork_db;
wasm_interface wasmif;
resource_limits_manager resource_limits;
authorization_manager authorization;
...
/**
* Transactions that were undone by pop_block or abort_block, transactions
* are removed from this list if they are re-applied in other blocks. Producers
* can query this list when scheduling new transactions into blocks.
*/
/**transaction的撤销由pop_block或abort_block来完成。如果有其他块重新应用了这些事物,则需要从该列表中将其删除。
* 当新transaction被调度成块是,用户可以查询列表。
* 从后面的分析中可以看到,abort_block并没有完成撤销工作
*/
map<digest_type,transaction_metadata_ptr> unapplied_transactions;
.
.
.
}
controller的初始化工作是由chain_plugin::plugin_initialize函数来完成的:检查白名单、黑名单、灰名单,数据库目录、检查点、及命令行参数的检查,主要功能定义在:plugins/chain_plugin/chain_plugin.cpp 314行。
在chain_plugin中还负责相关channel的初始化工作。
然后chain_plugin::plugin_start函数会将controller启动,定义在:plugins/chain_plugin/chain_plugin.cpp 633行:
try {
try {
//controller启动
my->chain->startup();
} catch (const database_guard_exception& e) {
log_guard_exception(e);
// make sure to properly close the db
my->chain.reset();
throw;
}
if(!my->readonly) {
ilog("starting chain in read/write mode");
}
ilog("Blockchain started; head block is #${num}, genesis timestamp is ${ts}",
("num", my->chain->head_block_num())("ts", (std::string)my->chain_config->genesis.initial_timestamp));
my->chain_config.reset();
} FC_CAPTURE_AND_RETHROW()
在controller::startup中会调用controller_impl::add_index:
这个函数主要为controller_impl::reversible_block和db添加索引:
//为reversible block建立索引
reversible_blocks.add_index<reversible_block_index>();
db.add_index<account_index>();
db.add_index<account_sequence_index>();
db.add_index<table_id_multi_index>();
db.add_index<key_value_index>();
db.add_index<index64_index>();
db.add_index<index128_index>();
db.add_index<index256_index>();
db.add_index<index_double_index>();
db.add_index<index_long_double_index>();
db.add_index<global_property_multi_index>();
db.add_index<dynamic_global_property_multi_index>();
db.add_index<block_summary_multi_index>();
db.add_index<transaction_multi_index>();
db.add_index<generated_transaction_multi_index>();
authorization.add_indices();
resource_limits.add_indices();
上述结构在后文有详细说明;然后进行fork_db的初始化工作,设置controller_impl::head,使其处于正确的状态为后续的区块生产做准备工作,到这里区块的初始化基本完成了,下面就到了区块生产的环节了。
从上文我们知道producer_plugin::start_block最后会调用controller::abort_block和start_block两个函数,这两个函数最终会调用controller_impl::abort_block和controller_impl::start_block两个函数:
controller_impl::abort_block重置controller_impl::pending信息,使pending处于全新状态:
if( pending ) {
//这里只是将_pending_block_state中的transaction重新放到unapplied_transactions中,并没有做撤销工作
if ( read_mode == db_read_mode::SPECULATIVE ) {
for( const auto& t : pending->_pending_block_state->trxs )
unapplied_transactions[t->signed_id] = t;
}
pending.reset();
}
controller_impl::start_block函数接受三个参数:1.即将要产生的区块的时间戳when,2.区块确认数量confirm_block_count,3.区块当前的状态status:
-
判断controller_impl::pending是否为初始状态,否则抛出异常
EOS_ASSERT( !pending, block_validate_exception, "pending block already exists" );
-
建立db session
if (!self.skip_db_sessions(s)) {
EOS_ASSERT( db.revision() == head->block_num, database_exception, "db revision is not on par with head block",
("db.revision()", db.revision())("controller_head_block", head->block_num)("fork_db_head_block", fork_db.head()->block_num) );
pending.emplace(maybe_session(db));
} else {
pending.emplace(maybe_session());
}
-
根据最近的controller_impl::head生成新的pending
pending->_block_status = s;
//这里会调用block_head::block_head(const block_header_state& prev, block_timestamp_type when)
//然后调用block_state_head::generate_next根据传进来的时间戳when生成新的block_header_state(新块)
//应为当前节点是正在出块的节点,所以在generate_next不需要对块进行完整性验证
//在同步块的时候则需要调用next函数,并做完整性验证后面详述
//generate_next代码定义在 libraries/chain/block_header_state.cpp 36行
pending->_pending_block_state = std::make_shared<block_state>( *head, when ); // promotes pending schedule (if any) to active
pending->_pending_block_state->in_current_chain = true;
-
将出块action打进transaction并执行,然后清理过期的transactions更新生产者授权
try {
auto onbtrx = std::make_shared<transaction_metadata>( get_on_block_transaction() );
onbtrx->implicit = true;
auto reset_in_trx_requiring_checks = fc::make_scoped_exit([old_value=in_trx_requiring_checks,this](){
in_trx_requiring_checks = old_value;
});
in_trx_requiring_checks = true;
push_transaction( onbtrx, fc::time_point::maximum(), self.get_global_properties().configuration.min_transaction_cpu_usage, true );
} catch( const boost::interprocess::bad_alloc& e ) {
elog( "on block transaction failed due to a bad allocation" );
throw;
} catch( const fc::exception& e ) {
wlog( "on block transaction failed, but shouldn't impact block generation, system contract needs update" );
edump((e.to_detail_string()));
} catch( ... ) {
}
clear_expired_input_transactions();
update_producers_authority();
至此controller_impl::start_block函数分析完毕,其主要功能就是根据当前head生成新块,并将出块action打进transaction中。
在controller_impl::start_block函数执行完毕候,控制权就交还给producer_plugin_impl::start_block了,在上文有对应的分析,producer_plugin_impl::start_block最终会把控制权交给producer_plugin_impl::schedule_production_loop,在这个函数中会启动一个定时器,在延迟一段时间之后会调用proudcer_plugin_impl::maybe_produce_block,这个函数会调用producer_plugin_impl::produce_block这在上文都有分析到,在producer_plugin_impl::produce_block中会调用:
controller::finalize_block,controller::sign_block和controller::commit_block三个函数来完成区块生产,区块签名,区块上链过程,下面来一次分析这三个函数:
-
controller::finalize_block
这个函数主要是完成资源更新包括生产该区块所使用的cpu资源,带宽资源;设置action merkle树根;设置transaction merkle树根,创建block summary信息:
resource_limits.process_account_limit_updates();
const auto& chain_config = self.get_global_properties().configuration;
uint32_t max_virtual_mult = 1000;
uint64_t CPU_TARGET = EOS_PERCENT(chain_config.max_block_cpu_usage, chain_config.target_block_cpu_usage_pct);
resource_limits.set_block_parameters(
{ CPU_TARGET, chain_config.max_block_cpu_usage, config::block_cpu_usage_average_window_ms / config::block_interval_ms, max_virtual_mult, {99, 100}, {1000, 999}},
{EOS_PERCENT(chain_config.max_block_net_usage, chain_config.target_block_net_usage_pct), chain_config.max_block_net_usage, config::block_size_average_window_ms / config::block_interval_ms, max_virtual_mult, {99, 100}, {1000, 999}}
);
resource_limits.process_block_usage(pending->_pending_block_state->block_num);
//设置action merkle树根
set_action_merkle();
//设置transaction merkle树根
set_trx_merkle();
auto p = pending->_pending_block_state;
p->id = p->header.id();
//根据block id生成 summary信息并放到数据库中
create_block_summary(p->id);
-
controller::sign_block
根据当前生产者提供的私钥签名函数对当前区块进行签名,并对做一次签名验证。
auto p = pending->_pending_block_state;
p->sign( signer_callback );
static_cast<signed_block_header&>(*p->block) = p->header;
block_header_state::sign(上面p->sign)定义如下:
auto d = sig_digest();
header.producer_signature = signer( d );
EOS_ASSERT( block_signing_key == fc::crypto::public_key( header.producer_signature, d ), wrong_signing_key, "block is signed with unexpected key" );
-
controller::commit_block
在详细分析这个函数之前需要先来分析一下fork_database这个类,它的结构如下:
struct by_block_id;
struct by_block_num;
struct by_lib_block_num;
struct by_prev;
//建立一个基于block_state_ptr的多索引容器
//by_block_id以block id为索引
//by_block_num 以区块高度为索引
//by_lib_block_num以最近的区块不可逆高度为索引
//by_prev以前一个block id为索引
typedef multi_index_container<
block_state_ptr,
indexed_by<
hashed_unique< tag<by_block_id>, member<block_header_state, block_id_type, &block_header_state::id>, std::hash<block_id_type>>,
ordered_non_unique< tag<by_prev>, const_mem_fun<block_header_state, const block_id_type&, &block_header_state::prev> >,
ordered_non_unique< tag<by_block_num>,
composite_key< block_state,
member<block_header_state,uint32_t,&block_header_state::block_num>,
member<block_state,bool,&block_state::in_current_chain>
>,
composite_key_compare< std::less<uint32_t>, std::greater<bool> >
>,
ordered_non_unique< tag<by_lib_block_num>,
composite_key< block_header_state,
member<block_header_state,uint32_t,&block_header_state::dpos_irreversible_blocknum>,
member<block_header_state,uint32_t,&block_header_state::bft_irreversible_blocknum>,
member<block_header_state,uint32_t,&block_header_state::block_num>
>,
composite_key_compare< std::greater<uint32_t>, std::greater<uint32_t>, std::greater<uint32_t> >
>
>
> fork_multi_index_type;
struct fork_database_impl {
fork_multi_index_type index;
block_state_ptr head; //区块头
fc::path datadir; //存储路径
}
class fork_database {
public:
//这里列举关键函数,详细定义参见 libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/fork_database.hpp
//根据区块id获取block_state信息
block_state_ptr get_block(const block_id_type &id) const;
//根据区块高度从当前链中获取block_state信息
block_state_ptr get_block_in_current_chain_by_num(uint32_t num) const;
//提供一个“有效的”区块状态,有可能以此建立分支
void set(block_state_ptr s);
block_state_ptr add(signed_block_ptr b,bool trust = false);
block_state_ptr add(block_state_ptr next_block);
void remove(const block_id_type &id);
void add(const header_confirmation &c);
const block_state_ptr &head() const;
//根据两个头block,获取两个分支(两个分支有共同的祖先,即两个头部的previous的值相同)
pair<branch_type,branch_type> fetch_branch_from(const block_id_type &first,const block_id_type &second) const;
//若该区块为invalid,将会从数据库中删除。若为valid,在发射irreversible信号后,所有比LIB大的block将会被修正
void set_validity(const block_state_ptr &h,bool valid);
void mark_in_current_chain(const block_state_ptr &h,bool in_current_chain);
void prune(const block_state_ptr&);
signal<void(block_state_ptr)> irreversible;
private:
void set_bft_irreversible(block_id_type id);
unique_ptr<for_database_impl> my;
}
回到controller_impl::commit_block,该接受一个bool参数,该参数表示是否需要将controller_impl::pending->_pending_block_state加入fork_database,如果是则将pending->_pending_block_state->validated设为true,然后调用fork_database::add(block_state_ptr)将该块加入数据库,然后会根据当前的block_state进行数据库数据修正(后文fork_database部分有详细分析),然后检查是否正在重演该区块,如果否则将其加入可以缓存reversible_blocks,发射accept_block信号,该信号会调用net_plugin_impl::accept_block,函数,这些信号量的设置定义在plugins/net_plugin/net_plugin.cpp 3017行:
```cpp
chain::controller&cc = my->chain_plug->chain();
{
cc.accepted_block_header.connect( boost::bind(&net_plugin_impl::accepted_block_header, my.get(), _1));
cc.accepted_block.connect( boost::bind(&net_plugin_impl::accepted_block, my.get(), _1));
cc.irreversible_block.connect( boost::bind(&net_plugin_impl::irreversible_block, my.get(), _1));
cc.accepted_transaction.connect( boost::bind(&net_plugin_impl::accepted_transaction, my.get(), _1));
cc.applied_transaction.connect( boost::bind(&net_plugin_impl::applied_transaction, my.get(), _1));
cc.accepted_confirmation.connect( boost::bind(&net_plugin_impl::accepted_confirmation, my.get(), _1));
}
commit_block关键代码如下:
try {
if (add_to_fork_db) {
pending->_pending_block_state->validated = true;
auto new_bsp = fork_db.add(pending->_pending_block_state);
emit(self.accepted_block_header, pending->_pending_block_state);
//更新head到最新生成的区块头
head = fork_db.head();
EOS_ASSERT(new_bsp == head, fork_database_exception, "committed block did not become the new head in fork database");
}
if( !replaying ) {
reversible_blocks.create<reversible_block_object>( [&]( auto& ubo ) {
ubo.blocknum = pending->_pending_block_state->block_num;
ubo.set_block( pending->_pending_block_state->block );
});
}
emit( self.accepted_block, pending->_pending_block_state );
} catch (...) {
// dont bother resetting pending, instead abort the block
reset_pending_on_exit.cancel();
abort_block();
throw;
}
至此controller_impl::commit_block工作完成。控制权回到producer_plugin_impl::produce_block,一次block生产调度就完成了,然后进入下一次调度。
fork_database分析:
结构如下:
struct by_block_id;
struct by_block_num;
struct by_lib_block_num;
struct by_prev;
//建立一个基于block_state_ptr的多索引容器
//by_block_id以block id为索引
//by_block_num 以区块高度为索引,组合键<block_num,in_current_chain>,降序
//by_lib_block_num以最近的区块不可逆高度为索引,组合键<dpos_irreversible_blocknum,bft_irreversible_blocknum,block_num>,升序
//by_prev以前一个block id为索引
typedef multi_index_container<
block_state_ptr,
indexed_by<
hashed_unique< tag<by_block_id>, member<block_header_state, block_id_type, &block_header_state::id>, std::hash<block_id_type>>,
ordered_non_unique< tag<by_prev>, const_mem_fun<block_header_state, const block_id_type&, &block_header_state::prev> >,
ordered_non_unique< tag<by_block_num>,
composite_key< block_state,
member<block_header_state,uint32_t,&block_header_state::block_num>,
member<block_state,bool,&block_state::in_current_chain>
>,
composite_key_compare< std::less<uint32_t>, std::greater<bool> >
>,
ordered_non_unique< tag<by_lib_block_num>,
composite_key< block_header_state,
member<block_header_state,uint32_t,&block_header_state::dpos_irreversible_blocknum>,
member<block_header_state,uint32_t,&block_header_state::bft_irreversible_blocknum>,
member<block_header_state,uint32_t,&block_header_state::block_num>
>,
composite_key_compare< std::greater<uint32_t>, std::greater<uint32_t>, std::greater<uint32_t> >
>
>
> fork_multi_index_type;
struct fork_database_impl {
fork_multi_index_type index;
block_state_ptr head; //区块头
fc::path datadir; //存储路径
}
class fork_database {
public:
//这里列举关键函数,详细定义参见 libraries/chain/include/eosio/chain/fork_database.hpp
//根据区块id获取block_state信息
block_state_ptr get_block(const block_id_type &id) const;
//根据区块高度从当前链中获取block_state信息
block_state_ptr get_block_in_current_chain_by_num(uint32_t num) const;
//提供一个“有效的”区块状态,有可能以此建立分支
void set(block_state_ptr s);
block_state_ptr add(signed_block_ptr b,bool trust = false);
block_state_ptr add(block_state_ptr next_block);
void remove(const block_id_type &id);
void add(const header_confirmation &c);
const block_state_ptr &head() const;
//根据两个头block,获取两个分支(两个分支有共同的祖先,即两个头部的previous的值相同)
pair<branch_type,branch_type> fetch_branch_from(const block_id_type &first,const block_id_type &second) const;
//若该区块为invalid,将会从数据库中删除。若为valid,在发射irreversible信号后,所有比LIB大的block将会被修正
void set_validity(const block_state_ptr &h,bool valid);
void mark_in_current_chain(const block_state_ptr &h,bool in_current_chain);
void prune(const block_state_ptr&);
signal<void(block_state_ptr)> irreversible;
private:
void set_bft_irreversible(block_id_type id);
unique_ptr<for_database_impl> my;
}
下面一次解释每个函数的实现:
-
void fork_database::set(block_state_ptr s)
//将s插入多索引容器中
auto result = my->index.insert( s );
EOS_ASSERT( s->id == s->header.id(), fork_database_exception,
"block state id (${id}) is different from block state header id (${hid})", ("id", string(s->id))("hid", string(s->header.id())) );
//FC_ASSERT( s->block_num == s->header.block_num() );
EOS_ASSERT( result.second, fork_database_exception, "unable to insert block state, duplicate state detected" );
//更新head状态
if( !my->head ) {
my->head = s;
} else if( my->head->block_num < s->block_num ) {
my->head = s;
}
-
-
-
transaction执行,涉及到的关键数据结构如下:
struct action_receipt {
account_name receiver; //执行该action的account
digest_type act_digest;
uint64_t global_sequence = 0;
uint64_t recv_sequence = 0;
flat_map<account_name,uint64_t> auth_sequence;
fc::unsigned_int code_sequence;
fc::unsigned_int abi_sequence;
};
struct base_action_trace {
action_receipt receipt;
action act;
fc::microseconds elapsed;
uint64_t cpu_usage = 0;
string console;
uint64_t total_cpu_usage = 0;
transaction_id_type trx_id;
}
struct action_trace : public base_action_trace {
vector<action_trace> inline_traces;
}
struct transaction_trace {
transaction_id_type id;
fc::optional<transaction_receipt_header> receipt;
fc::microseconds elapsed;
uint64_t net_usage;
bool scheduled = false;
vector<action_trace> action_traces;
transaction_trace_ptr failed_dtrx_trace;
fc::optional<fc::exception> except;
std::exception_ptr except_ptr;
}
一个transaction是由一个或多个action组成的,这些action如果又一个失败了,那么该transaction也就失败了,已经执行过的action需要回滚。每个transaction必须在30ms内完成,如果一个包含了多个action且这些action执行时间总和超过30ms,则整个transaction失败。
chainbase分析
database基本数据结构
和数据库相关的数据结构均派生自 struct object,结构如下:
template<typename T>
class oid {
public:
oid( int64_t i = 0 ):_id{i}{}
oid& operator++() {
++_id;
return *this;
}
friend bool operator < ( const oid& a,const oid& b ) {
return a._id < b._id;
}
friend bool operator > ( const oid& a,const oid& b ) {
return a._id > b._id;
}
friend bool operator == ( const oid& a,const oid& b ) {
return a._id == b._id;
}
friend bool operator != ( const oid& a,const oid& b ) {
return a._id != b._id;
}
friend std::ostream& operator << ( std::ostream& s,const oid& id ) {
s << boost::core::demangle( typeid( oid<T> ).name() ) << '(' << id._id << ')';
return s;
}
int64_t _id;
};
template<uint16_t TypeNumber,typename Derived>
struct object {
typedef oid<Derived> id_type;
static const uint16_t type_id = TypeNumber; //类型标识
};
数据库的索引是通过元编程来实现的,每一种数据类型都有一个唯一id作为标识。程序在运行过程中要产生27个数据表:
-
account_object:
保存账户信息,结构如下:
class account_object : public chainbase::object<account_object_type,account_objct> {
OBJECT_CTOR(account_object,(code)(abi))
id_type id;
account_name name; //账户名称base32编码
uint8_t vm_type = 0; // vm_type
uint8_t vm_version = 0; // vm_version
bool privileged = false; // 是否优先
time_point last_code_update; //上次参与权限验证的时间
digest_type code_version;
block_timestamp_type creation_date; //创建时间
shared_string code;
shared_string abi;
void set_abi( const eosio::chain::abi_def& a ) {
abi.resize( fc::raw::pack_size( a ) );
fc::datastream<char*> ds( abi.data(), abi.size() );
fc::raw::pack( ds, a );
}
eosio::chain::abi_def get_abi()const {
eosio::chain::abi_def a;
EOS_ASSERT( abi.size() != 0, abi_not_found_exception, "No ABI set on account ${n}", ("n",name) );
fc::datastream<const char*> ds( abi.data(), abi.size() );
fc::raw::unpack( ds, a );
return a;
}
};
其中宏OBJECT_CTOR(account_object,(code)(abi))展开如下:
account_object() = delete;
public:
template<typename Constructor, typename Allocator>
account_object(Constructor&& c, chainbase::allocator<Allocator> a) : id(0) ,code(a) ,abi(a) { c(*this); }
该结构保存了账户的信息,对应的多索引容器为:
struct by_name;
using account_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
account_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag<by_id>, member<account_object, account_object::id_type, &account_object::id>>,
ordered_unique<tag<by_name>, member<account_object, account_name, &account_object::name>>
>
>;
创建一个账户的函数调用在libraries/chain/eos_contract.cpp void apply_eosio_newaccount(apply_context& context)函数中.
-
account_sequence_object
这个结构用来存储和账户相关的序列数据,具体结构如下:
class account_sequence_object : public chainbase::object<account_sequence_object_type, account_sequence_object>
{
OBJECT_CTOR(account_sequence_object);
id_type id;
account_name name;
uint64_t recv_sequence = 0;
uint64_t auth_sequence = 0;
uint64_t code_sequence = 0;
uint64_t abi_sequence = 0;
};
对应的多索引容器如下:
struct by_name;
using account_sequence_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
account_sequence_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag<by_id>, member<account_sequence_object, account_sequence_object::id_type, &account_sequence_object::id>>,
ordered_unique<tag<by_name>, member<account_sequence_object, account_name, &account_sequence_object::name>>
>
>;
-
permission_object
用来存储授权相关信息,具体结构如下:
class permission_object : public chainbase::object<permission_object_type, permission_object> {
OBJECT_CTOR(permission_object, (auth) )
id_type id;
permission_usage_object::id_type usage_id;
id_type parent; ///< parent permission
account_name owner; ///< the account this permission belongs to
permission_name name; ///< human-readable name for the permission
time_point last_updated; ///< the last time this authority was updated
shared_authority auth; ///< authority required to execute this permission
/**
* @brief Checks if this permission is equivalent or greater than other
* @tparam Index The permission_index
* @return true if this permission is equivalent or greater than other, false otherwise
*
* Permissions are organized hierarchically such that a parent permission is strictly more powerful than its
* children/grandchildren. This method checks whether this permission is of greater or equal power (capable of
* satisfying) permission @ref other.
*/
template <typename Index>
bool satisfies(const permission_object& other, const Index& permission_index) const {
// If the owners are not the same, this permission cannot satisfy other
if( owner != other.owner )
return false;
// If this permission matches other, or is the immediate parent of other, then this permission satisfies other
if( id == other.id || id == other.parent )
return true;
// Walk up other's parent tree, seeing if we find this permission. If so, this permission satisfies other
const permission_object* parent = &*permission_index.template get<by_id>().find(other.parent);
while( parent ) {
if( id == parent->parent )
return true;
if( parent->parent._id == 0 )
return false;
parent = &*permission_index.template get<by_id>().find(parent->parent);
}
// This permission is not a parent of other, and so does not satisfy other
return false;
}
};
对应的多索引容器为:
struct by_parent;
struct by_owner;
struct by_name;
using permission_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
permission_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag<by_id>, member<permission_object, permission_object::id_type, &permission_object::id>>,
ordered_unique<tag<by_parent>,
composite_key<permission_object,
member<permission_object, permission_object::id_type, &permission_object::parent>,
member<permission_object, permission_object::id_type, &permission_object::id>
>
>,
ordered_unique<tag<by_owner>,
composite_key<permission_object,
member<permission_object, account_name, &permission_object::owner>,
member<permission_object, permission_name, &permission_object::name>
>
>,
ordered_unique<tag<by_name>,
composite_key<permission_object,
member<permission_object, permission_name, &permission_object::name>,
member<permission_object, permission_object::id_type, &permission_object::id>
>
>
>
>;
-
permission_usage_object
保存了授权的使用信息,具体结构如下:
class permission_usage_object : public chainbase::object<permission_usage_object_type, permission_usage_object> {
OBJECT_CTOR(permission_usage_object)
id_type id;
time_point last_used; ///< when this permission was last used
};
对应的多索引容器为:
struct by_account_permission;
using permission_usage_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
permission_usage_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag<by_id>, member<permission_usage_object, permission_usage_object::id_type, &permission_usage_object::id>>
>
>;
-
permission_link_object
这个类记录了contract 和 action之间的permission_object的链接,以记录这些contract在执行的过程中所需要的权限
class permission_link_object : public chainbase::object<permission_link_object_type, permission_link_object> {
OBJECT_CTOR(permission_link_object)
id_type id;
/// The account which is defining its permission requirements
account_name account;
/// The contract which account requires @ref required_permission to invoke
account_name code; /// TODO: rename to scope
/// The message type which account requires @ref required_permission to invoke
/// May be empty; if so, it sets a default @ref required_permission for all messages to @ref code
action_name message_type;
/// The permission level which @ref account requires for the specified message types
permission_name required_permission;
};
对应的索引如下:
struct by_action_name;
struct by_permission_name;
using permission_link_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
permission_link_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag<by_id>,
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(permission_link_object, permission_link_object::id_type, id)
>,
ordered_unique<tag<by_action_name>,
composite_key<permission_link_object,
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(permission_link_object, account_name, account),
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(permission_link_object, account_name, code),
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(permission_link_object, action_name, message_type)
>
>,
ordered_unique<tag<by_permission_name>,
composite_key<permission_link_object,
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(permission_link_object, account_name, account),
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(permission_link_object, permission_name, required_permission),
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(permission_link_object, account_name, code),
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(permission_link_object, action_name, message_type)
>
>
>
>;
-
key_value_object
结构如下:
struct key_value_object : public chainbase::object<key_value_object_type, key_value_object> {
OBJECT_CTOR(key_value_object, (value))
typedef uint64_t key_type;
static const int number_of_keys = 1;
id_type id;
table_id t_id;
uint64_t primary_key; //主键
account_name payer = 0;
shared_string value; //值
};
对应的索引:
using key_value_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
key_value_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag<by_id>, member<key_value_object, key_value_object::id_type, &key_value_object::id>>,
ordered_unique<tag<by_scope_primary>,
composite_key< key_value_object,
member<key_value_object, table_id, &key_value_object::t_id>,
member<key_value_object, uint64_t, &key_value_object::primary_key>
>,
composite_key_compare< std::less<table_id>, std::less<uint64_t> >
>
>
>;
-
index64_object
是基于多索引容器建立的一个二级索引,定义如下:
typedef secondary_index<uint64_t,index64_object_type>::index_object index64_object;
typedef secondary_index<uint64_t,index64_object_type>::index_index index64_index;
-
index128_object
同上
-
index256_object
同上
-
index_double_object
同上
-
index_long_double_object
同上
-
global_property_object
存储了初始设定的值,用来调用块参数:
class global_property_object : public chainbase::object<global_property_object_type, global_property_object>
{
OBJECT_CTOR(global_property_object, (proposed_schedule))
id_type id;
optional<block_num_type> proposed_schedule_block_num;
shared_producer_schedule_type proposed_schedule;
chain_config configuration;
};
对应的索引:
using dynamic_global_property_multi_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
dynamic_global_property_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag<by_id>,
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(dynamic_global_property_object, dynamic_global_property_object::id_type, id)
>
>
>;
-
dynamic_global_property_object
记录了区块链正常操作期间所计算的值,这些值反映了区块链的当前的全局的值:
class dynamic_global_property_object : public chainbase::object<dynamic_global_property_object_type, dynamic_global_property_object>
{
OBJECT_CTOR(dynamic_global_property_object)
id_type id;
uint64_t global_action_sequence = 0;
};
对应的索引为:
using global_property_multi_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
global_property_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag,
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(global_property_object, global_property_object::id_type, id)
;
14. block_summary_object
block的一个简明信息,用于transaction的TaPos验证。结构如下:
class block_summary_object : public chainbase::object<block_summary_object_type, block_summary_object>
{
OBJECT_CTOR(block_summary_object)
id_type id;
block_id_type block_id;
};
```
对应的索引为:
```
struct by_block_id;
using block_summary_multi_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
block_summary_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag<by_id>, BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(block_summary_object, block_summary_object::id_type, id)>
// ordered_unique<tag<by_block_id>, BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(block_summary_object, block_id_type, block_id)>
>
>;
```
在controller::finalize_block函数中,会产生一个该结构的记录:
```
set_action_merkle();
set_trx_merkle();
auto p = pending->_pending_block_state;
p->id = p->header.id();
create_block_summary(p->id); //创建一个block_summary
```
-
transaction_object
记录了transaction的过期时间,在该过期时间内,如果该transaction还没得倒确认,则会删除:
class transaction_object : public chainbase::object<transaction_object_type, transaction_object>
{
OBJECT_CTOR(transaction_object)
id_type id;
time_point_sec expiration;
transaction_id_type trx_id;
};
对应的索引为:
struct by_expiration;
struct by_trx_id;
using transaction_multi_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
transaction_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique< tag<by_id>, BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(transaction_object, transaction_object::id_type, id)>,
ordered_unique< tag<by_trx_id>, BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(transaction_object, transaction_id_type, trx_id)>,
ordered_unique< tag<by_expiration>,
composite_key< transaction_object,
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER( transaction_object, time_point_sec, expiration ),
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER( transaction_object, transaction_object::id_type, id)
>
>
>
>;
在transaction执行的时候,会对收到的transaction做一个初始化工作,transaction_context::init_for_input_trx会调用该函数产生一个transaction_object记录:
published = control.pending_block_time();
is_input = true;
if (!control.skip_trx_checks()) {
control.validate_expiration(trx);
control.validate_tapos(trx);
control.validate_referenced_accounts(trx);
}
init( initial_net_usage);
if (!skip_recording)
record_transaction( id, trx.expiration ); /// checks for dupes
-
generated_transaction_object
结构如下:
class generated_transaction_object : public chainbase::object<generated_transaction_object_type, generated_transaction_object>
{
OBJECT_CTOR(generated_transaction_object, (packed_trx) )
id_type id;
transaction_id_type trx_id;
account_name sender;
uint128_t sender_id = 0; /// ID given this transaction by the sender
account_name payer;
time_point delay_until; /// this generated transaction will not be applied until the specified time
time_point expiration; /// this generated transaction will not be applied after this time
time_point published;
shared_string packed_trx;
uint32_t set( const transaction& trx ) {
auto trxsize = fc::raw::pack_size( trx );
packed_trx.resize( trxsize );
fc::datastream<char*> ds( packed_trx.data(), trxsize );
fc::raw::pack( ds, trx );
return trxsize;
}
};
对应的索引:
struct by_trx_id;
struct by_expiration;
struct by_delay;
struct by_status;
struct by_sender_id;
using generated_transaction_multi_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
generated_transaction_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique< tag, BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(generated_transaction_object, generated_transaction_object::id_type, id)>,
ordered_unique< tag, BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER( generated_transaction_object, transaction_id_type, trx_id)>,
ordered_unique< tag,
composite_key< generated_transaction_object,
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER( generated_transaction_object, time_point, expiration),
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER( generated_transaction_object, generated_transaction_object::id_type, id)
,
ordered_unique< tag,
composite_key< generated_transaction_object,
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER( generated_transaction_object, time_point, delay_until),
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER( generated_transaction_object, generated_transaction_object::id_type, id)
,
ordered_unique< tag,
composite_key< generated_transaction_object,
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER( generated_transaction_object, account_name, sender),
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER( generated_transaction_object, uint128_t, sender_id)
;
17. producer_object
结构如下:
class producer_object : public chainbase::object<producer_object_type, producer_object> {
OBJECT_CTOR(producer_object)
id_type id;
account_name owner;
uint64_t last_aslot = 0;
public_key_type signing_key;
int64_t total_missed = 0;
uint32_t last_confirmed_block_num = 0;
/// The blockchain configuration values this producer recommends
chain_config configuration;
};
对应的索引:
struct by_key;
struct by_owner;
using producer_multi_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
producer_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag, member<producer_object, producer_object::id_type, &producer_object::id>>,
ordered_unique<tag, member<producer_object, account_name, &producer_object::owner>>,
ordered_unique<tag,
composite_key<producer_object,
member<producer_object, public_key_type, &producer_object::signing_key>,
member<producer_object, producer_object::id_type, &producer_object::id>
;
18. account_control_history_object
19. public_key_history_object
20. table_id_object
结构如下:
class table_id_object : public chainbase::object<table_id_object_type, table_id_object> {
OBJECT_CTOR(table_id_object)
id_type id;
account_name code;
scope_name scope;
table_name table;
account_name payer;
uint32_t count = 0; /// the number of elements in the table
};
对应的索引:
struct by_code_scope_table;
using table_id_multi_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
table_id_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag,
member<table_id_object, table_id_object::id_type, &table_id_object::id>
,
ordered_unique<tag,
composite_key< table_id_object,
member<table_id_object, account_name, &table_id_object::code>,
member<table_id_object, scope_name, &table_id_object::scope>,
member<table_id_object, table_name, &table_id_object::table>
;
21. resource_limits_object
结构如下:
struct resource_limits_object : public chainbase::object<resource_limits_object_type, resource_limits_object> {
OBJECT_CTOR(resource_limits_object)
id_type id;
account_name owner;
bool pending = false;
int64_t net_weight = -1;
int64_t cpu_weight = -1;
int64_t ram_bytes = -1;
};
对应的索引:
struct by_owner;
struct by_dirty;
using resource_limits_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
resource_limits_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag, member<resource_limits_object, resource_limits_object::id_type, &resource_limits_object::id>>,
ordered_unique<tag,
composite_key<resource_limits_object,
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(resource_limits_object, bool, pending),
BOOST_MULTI_INDEX_MEMBER(resource_limits_object, account_name, owner)
;
22. resource_usage_object
结构如下:
struct resource_usage_object : public chainbase::object<resource_usage_object_type, resource_usage_object> {
OBJECT_CTOR(resource_usage_object)
id_type id;
account_name owner;
usage_accumulator net_usage;
usage_accumulator cpu_usage;
uint64_t ram_usage = 0;
};
对应的索引:
using resource_usage_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
resource_usage_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag, member<resource_usage_object, resource_usage_object::id_type, &resource_usage_object::id>>,
ordered_unique<tag, member<resource_usage_object, account_name, &resource_usage_object::owner> >
;
23. resource_limits_config_object
结构如下:
class resource_limits_config_object : public chainbase::object<resource_limits_config_object_type, resource_limits_config_object> {
OBJECT_CTOR(resource_limits_config_object);
id_type id;
static_assert( config::block_interval_ms > 0, "config::block_interval_ms must be positive" );
static_assert( config::block_cpu_usage_average_window_ms >= config::block_interval_ms,
"config::block_cpu_usage_average_window_ms cannot be less than config::block_interval_ms" );
static_assert( config::block_size_average_window_ms >= config::block_interval_ms,
"config::block_size_average_window_ms cannot be less than config::block_interval_ms" );
elastic_limit_parameters cpu_limit_parameters = {EOS_PERCENT(config::default_max_block_cpu_usage, config::default_target_block_cpu_usage_pct), config::default_max_block_cpu_usage, config::block_cpu_usage_average_window_ms / config::block_interval_ms, 1000, {99, 100}, {1000, 999}};
elastic_limit_parameters net_limit_parameters = {EOS_PERCENT(config::default_max_block_net_usage, config::default_target_block_net_usage_pct), config::default_max_block_net_usage, config::block_size_average_window_ms / config::block_interval_ms, 1000, {99, 100}, {1000, 999}};
uint32_t account_cpu_usage_average_window = config::account_cpu_usage_average_window_ms / config::block_interval_ms;
uint32_t account_net_usage_average_window = config::account_net_usage_average_window_ms / config::block_interval_ms;
};
对应的索引:
using resource_limits_config_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
resource_limits_config_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag, member<resource_limits_config_object, resource_limits_config_object::id_type, &resource_limits_config_object::id>>
;
24. resource_limits_state_object
class resource_limits_state_object : public chainbase::object<resource_limits_state_object_type, resource_limits_state_object> {
OBJECT_CTOR(resource_limits_state_object);
id_type id;
/**
* Track the average netusage for blocks
*/
usage_accumulator average_block_net_usage;
/**
* Track the average cpu usage for blocks
*/
usage_accumulator average_block_cpu_usage;
void update_virtual_net_limit( const resource_limits_config_object& cfg );
void update_virtual_cpu_limit( const resource_limits_config_object& cfg );
uint64_t pending_net_usage = 0ULL;
uint64_t pending_cpu_usage = 0ULL;
uint64_t total_net_weight = 0ULL;
uint64_t total_cpu_weight = 0ULL;
uint64_t total_ram_bytes = 0ULL;
/**
* The virtual number of bytes that would be consumed over blocksize_average_window_ms
* if all blocks were at their maximum virtual size. This is virtual because the
* real maximum block is less, this virtual number is only used for rate limiting users.
*
* It's lowest possible value is max_block_size * blocksize_average_window_ms / block_interval
* It's highest possible value is 1000 times its lowest possible value
*
* This means that the most an account can consume during idle periods is 1000x the bandwidth
* it is gauranteed under congestion.
*
* Increases when average_block_size < target_block_size, decreases when
* average_block_size > target_block_size, with a cap at 1000x max_block_size
* and a floor at max_block_size;
**/
uint64_t virtual_net_limit = 0ULL;
/**
* Increases when average_bloc
*/
uint64_t virtual_cpu_limit = 0ULL;
};
对应的索引:
using resource_limits_state_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
resource_limits_state_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag, member<resource_limits_state_object, resource_limits_state_object::id_type, &resource_limits_state_object::id>>
;
25. account_history_object
26. action_history_object
27. reversible_block_object
记录还没变成不可逆的区块,结构如下:
class reversible_block_object : public chainbase::object<reversible_block_object_type, reversible_block_object> {
OBJECT_CTOR(reversible_block_object,(packedblock) )
id_type id;
uint32_t blocknum = 0;
shared_string packedblock;
void set_block( const signed_block_ptr& b ) {
packedblock.resize( fc::raw::pack_size( *b ) );
fc::datastream<char*> ds( packedblock.data(), packedblock.size() );
fc::raw::pack( ds, *b );
}
signed_block_ptr get_block()const {
fc::datastream<const char*> ds( packedblock.data(), packedblock.size() );
auto result = std::make_shared<signed_block>();
fc::raw::unpack( ds, *result );
return result;
}
};
对应的索引为:
struct by_num;
using reversible_block_index = chainbase::shared_multi_index_container<
reversible_block_object,
indexed_by<
ordered_unique<tag, member<reversible_block_object, reversible_block_object::id_type, &reversible_block_object::id>>,
ordered_unique<tag, member<reversible_block_object, uint32_t, &reversible_block_object::blocknum>>
;
以上数据表的初始化工作在controller_impl::add_indices()函数中:
reversible_blocks.add_index<reversible_block_index>();
db.add_index<account_index>();
db.add_index<account_sequence_index>();
db.add_index<table_id_multi_index>();
db.add_index<key_value_index>();
db.add_index<index64_index>();
db.add_index<index128_index>();
db.add_index<index256_index>();
db.add_index<index_double_index>();
db.add_index<index_long_double_index>();
db.add_index<global_property_multi_index>();
db.add_index<dynamic_global_property_multi_index>();
db.add_index<block_summary_multi_index>();
db.add_index<transaction_multi_index>();
db.add_index<generated_transaction_multi_index>();
authorization.add_indices();
resource_limits.add_indices();
在authorization_manager::add_indices():
_db.add_index<permission_index>();
_db.add_index<permission_usage_index>();
_db.add_index<permission_link_index>();
在resource_limits_manager::add_indices():
_db.add_index<resource_limits_index>();
_db.add_index<resource_usage_index>();
_db.add_index<resource_limits_state_index>();
_db.add_index<resource_limits_config_index>();
在transaction执行过程中涉及到的数据及流程如下:
调用controller_impl::push_transaction,在该函数中会生成一个transaction_context类型的变量trx_context, 然后对transaction进行初始化操作:
transaction_context trx_context(self, trx->trx, trx->id);
if ((bool)subjective_cpu_leeway && pending->_block_status == controller::block_status::incomplete) {
trx_context.leeway = *subjective_cpu_leeway;
}
trx_context.deadline = deadline;
trx_context.explicit_billed_cpu_time = explicit_billed_cpu_time;
trx_context.billed_cpu_time_us = billed_cpu_time_us;
trace = trx_context.trace;
try {
if( trx->implicit ) {
trx_context.init_for_implicit_trx();
trx_context.can_subjectively_fail = false;
} else {
bool skip_recording = replay_head_time && (time_point(trx->trx.expiration) <= *replay_head_time);
trx_context.init_for_input_trx( trx->packed_trx.get_unprunable_size(),
trx->packed_trx.get_prunable_size(),
trx->trx.signatures.size(),
skip_recording);
}
if( trx_context.can_subjectively_fail && pending->_block_status == controller::block_status::incomplete ) {
check_actor_list( trx_context.bill_to_accounts ); // Assumes bill_to_accounts is the set of actors authorizing the transaction
}
trx_context.delay = fc::seconds(trx->trx.delay_sec);
然后对transaction进行授权检查:
if( !self.skip_auth_check() && !trx->implicit ) {
authorization.check_authorization(
trx->trx.actions,
trx->recover_keys( chain_id ),
{},
trx_context.delay,
[](){}
/*std::bind(&transaction_context::add_cpu_usage_and_check_time, &trx_context,
std::placeholders::_1)*/,
false
);
}
trx_context.exec();
trx_context.finalize(); /
在此需要用到上面的global_property_object数据表,然后调用transaction_context::exec()对action进行调用:
EOS_ASSERT( is_initialized, transaction_exception, "must first initialize" );
if( apply_context_free ) {
for( const auto& act : trx.context_free_actions ) {
trace->action_traces.emplace_back();
dispatch_action( trace->action_traces.back(), act, true );//action调用
}
}
if( delay == fc::microseconds() ) {
for( const auto& act : trx.actions ) {
trace->action_traces.emplace_back();
dispatch_action( trace->action_traces.back(), act ); //action调用
}
} else {
schedule_transaction();
}
在transaction_context::dispatch_action中会产生一个类型为apply_context的变量 acontext,调用apply_context::exec()进行真正的action的执行
apply_context acontext( control, *this, a, recurse_depth );
acontext.context_free = context_free;
acontext.receiver = receiver;
try {
acontext.exec();
} catch( ... ) {
trace = move(acontext.trace);
throw;
}
trace = move(acontext.trace);
在apply_context::exec()中会调用apply_context::exec_one() 调用vm借口进入合约层,进行action和数据的解析并执行。
vm会通过注册进入的借口来调用action执行,注册的借口为:
REGISTER_INTRINSICS(transaction_api,
(send_inline, void(int, int) )
(send_context_free_inline, void(int, int) )
(send_deferred, void(int, int64_t, int, int, int32_t) )
(cancel_deferred, int(int) )
);
transaction_api接口定义如下:
class transaction_api : public context_aware_api {
public:
using context_aware_api::context_aware_api;
void send_inline( array_ptr<char> data, size_t data_len ) {
//TODO: Why is this limit even needed? And why is it not consistently checked on actions in input or deferred transactions
EOS_ASSERT( data_len < context.control.get_global_properties().configuration.max_inline_action_size, inline_action_too_big,
"inline action too big" );
action act;
fc::raw::unpack<action>(data, data_len, act);
context.execute_inline(std::move(act));
}
void send_context_free_inline( array_ptr<char> data, size_t data_len ) {
//TODO: Why is this limit even needed? And why is it not consistently checked on actions in input or deferred transactions
EOS_ASSERT( data_len < context.control.get_global_properties().configuration.max_inline_action_size, inline_action_too_big,
"inline action too big" );
action act;
fc::raw::unpack<action>(data, data_len, act);
context.execute_context_free_inline(std::move(act));
}
void send_deferred( const uint128_t& sender_id, account_name payer, array_ptr<char> data, size_t data_len, uint32_t replace_existing) {
try {
transaction trx;
fc::raw::unpack<transaction>(data, data_len, trx);
context.schedule_deferred_transaction(sender_id, payer, std::move(trx), replace_existing);
} FC_RETHROW_EXCEPTIONS(warn, "data as hex: ${data}", ("data", fc::to_hex(data, data_len)))
}
bool cancel_deferred( const unsigned __int128& val ) {
fc::uint128_t sender_id(val>>64, uint64_t(val) );
return context.cancel_deferred_transaction( (unsigned __int128)sender_id );
}
};
以上为系统数据表和database交互的模式。
智能合约的持久化存储和database交互
说到智能合约的持久化存储离不开Multi-Index,这个Multi-index是EOS实现的类boost::multi_index_container的功能,定义在: contracts/eosiolib/multi_index.hpp文件中,采用的是hana元编程,我们写的智能合约中的数据就是存储在这个multi_index中的。
该类实现了数据的增删改查接口:emplace,erase,modify,get,find等接口,通过这些接口和database进行交互。
-
emplace中和database交互的关键代码:
datastream<char*> ds( (char*)buffer, size );
ds << obj;
auto pk = obj.primary_key();
//db_store_i64就是和database进行交互的接口
i.__primary_itr = db_store_i64( _scope, TableName, payer, pk, buffer, size );
if ( max_stack_buffer_size < size ) {
free(buffer);
}
-
erase中和database交互的关键代码:
eosio_assert( itr2 != _items_vector.rend(), "attempt to remove object that was not in multi_index" );
_items_vector.erase(--(itr2.base()));
//和database进行交互
db_remove_i64( objitem.__primary_itr );
其他接口和数据库交互请参看源码。
multi_index的使用:
class book_manager : public eosio::contract {
public:
void create()
void delete()
void find()
private:
account_name _contract_name;
struct book {
uint64_t _id;
std::string _name;
EOSLIB_SERIALIZE(book,(_id)(_name));
}
typedef eosio::multi_index<N(book),book> _table;
}
大概类似于上面的代码,后面我会出一个详细智能合约开发的例子。EOSLIB_SERIALIZE宏用于序列化book接口,将其转为字节数组。后面我就可以基于_table对book进行管理了,增删改查也会与database进行交互,现在来看一下database提供的api接口,这些接口定义在 libraries/chain/wasm_interface.cpp中:
class database_api : public context_aware_api {
public:
using context_aware_api::context_aware_api;
int db_store_i64( uint64_t scope, uint64_t table, uint64_t payer, uint64_t id, array_ptr<const char> buffer, size_t buffer_size ) {
return context.db_store_i64( scope, table, payer, id, buffer, buffer_size );
}
void db_update_i64( int itr, uint64_t payer, array_ptr<const char> buffer, size_t buffer_size ) {
context.db_update_i64( itr, payer, buffer, buffer_size );
}
void db_remove_i64( int itr ) {
context.db_remove_i64( itr );
}
int db_get_i64( int itr, array_ptr<char> buffer, size_t buffer_size ) {
return context.db_get_i64( itr, buffer, buffer_size );
}
int db_next_i64( int itr, uint64_t& primary ) {
return context.db_next_i64(itr, primary);
}
int db_previous_i64( int itr, uint64_t& primary ) {
return context.db_previous_i64(itr, primary);
}
int db_find_i64( uint64_t code, uint64_t scope, uint64_t table, uint64_t id ) {
return context.db_find_i64( code, scope, table, id );
}
int db_lowerbound_i64( uint64_t code, uint64_t scope, uint64_t table, uint64_t id ) {
return context.db_lowerbound_i64( code, scope, table, id );
}
int db_upperbound_i64( uint64_t code, uint64_t scope, uint64_t table, uint64_t id ) {
return context.db_upperbound_i64( code, scope, table, id );
}
int db_end_i64( uint64_t code, uint64_t scope, uint64_t table ) {
return context.db_end_i64( code, scope, table );
}
DB_API_METHOD_WRAPPERS_SIMPLE_SECONDARY(idx64, uint64_t)
DB_API_METHOD_WRAPPERS_SIMPLE_SECONDARY(idx128, uint128_t)
DB_API_METHOD_WRAPPERS_ARRAY_SECONDARY(idx256, 2, uint128_t)
DB_API_METHOD_WRAPPERS_FLOAT_SECONDARY(idx_double, float64_t)
DB_API_METHOD_WRAPPERS_FLOAT_SECONDARY(idx_long_double, float128_t)
} ;
由上可见database_api调用的是apply_context提供的接口,而appy_context中有database的引用,最终所有的操作都会反映到database中去
转载自:https://github.com/123youyouer/eosex/tree/master/block_chain